Old and New London: Volume 1. Originally published by Cassell, Petter & Galpin, London, 1878.
This free content was digitised by double rekeying. Public Domain.
Walter Thornbury, 'Cheapside: Introduction ', in Old and New London: Volume 1(London, 1878), British History Online https://prod.british-history.ac.uk/old-new-london/vol1/pp304-315 [accessed 19 April 2025].
Walter Thornbury, 'Cheapside: Introduction ', in Old and New London: Volume 1(London, 1878), British History Online, accessed April 19, 2025, https://prod.british-history.ac.uk/old-new-london/vol1/pp304-315.
Walter Thornbury. "Cheapside: Introduction ". Old and New London: Volume 1. (London, 1878), British History Online. Web. 19 April 2025. https://prod.british-history.ac.uk/old-new-london/vol1/pp304-315.
In this section
CHAPTER XXVI.
CHEAPSIDE—INTRODUCTORY AND HISTORICAL.
Ancient Reminiscences of Cheapside—Stormy Days therein—The Westchepe Market—Something about the Pillory—The Cheapside Conduits—The Goldsmiths' Monopoly—Cheapside Market—Gossip anent Cheapside by Mr. Pepys—A Saxon Rienzi—Anti-Free-Trade Riots in Cheapside—Arrest of the Rioters—A Royal Pardon—Jane Shore.
What a wealth and dignity there is about Cheapside; what restless life and energy; with what vigorous pulsation life beats to and fro in that great commercial artery ! How pleasantly on a summer morning that last of the Mohicans, the green plane-tree now deserted by the rooks, at the corner of Wood Street, flutters its leaves! How fast the crowded omnibuses dash past with their loads of young Greshams and future rulers of Lombard Street! How grandly Bow steeple bears itself, rising proudly in the sunshine! How the great webs of gold chains sparkle in the jeweller's windows! How modern everything looks, and yet only a short time since some workmen at a foundation in Cheapside, twenty-five feet below the surface, came upon traces of primeval inhabitants in the shape of a deer's skull, with antlers, and the skull of a wolf, struck down, perhaps, more than a thousand years ago, by the bronze axe of some British savage. So the world rolls on: the times change, and we change with them.
The engraving which we give on page 307 is from one of the most ancient representations extant of Cheapside. It shows the street decked out in holiday attire for the procession of the wicked old queen-mother, Marie de Medici, on her way to visit her son-in-law, Charles I., and her wilful daughter, Henrietta Maria.
The City records, explored with such unflagging interest by Mr. Riley in his "Memorials of London," furnish us with some interesting gleanings relating to Cheapside. In the old letter books in the Guildhall—the Black Book, Red Book, and White Book—we see it in storm and calm, observe the vigilant and jealous honesty of the guilds, and become witnesses again to the bloody frays, cruel punishments, and even the petty disputes of the middle-age craftsmen, when Cheapside was one glittering row of goldsmiths' shops, and the very heart of the wealth of London. The records culled so carefully by Mr. Riley are brief but pregnant; they give us facts uncoloured by the historian, and highly suggestive glimpses of strange modes of life in wild and picturesque eras of our civilisation. Let us take the most striking seriatim.
In 1273 the candle-makers seem to have taken a fancy to Cheapside, where the horrible fumes of that necessary but most offensive trade soon excited the ire of the rich citizens, who at last expelled seventeen of the craft from their sheds in Chepe. In the third year of Edward II. it was ordered and commanded on the king's behalf, that "no man or woman should be so bold as henceforward to hold common market for merchandise in Chepe, or any other highway within the City, except Cornhill, after the hour of nones" (probably about two p.m.); and the same year it was forbidden, under pain of imprisonment, to scour pots in the roadway of Chepe, to the hindrance of folks who were passing; so that we may conclude that in Edward II.'s London there was a good deal of that out-door work that the traveller still sees in the back streets of Continental towns.
Holocausts of spurious goods were not uncommon in Cheapside. In 1311 (Edward II.) we find that at the request of the hatters and haberdashers, search had been made for traders selling "bad and cheating hats," that is, of false and dishonest workmanship, made of a mixture of wool and flocks. The result was the seizure of forty grey and white hats, and fifteen black, which were publicly burnt in the street of Chepe. What a burning such a search would lead to in our less scrupulous days! Why, the pile would reach half way up St. Paul's. Illegal nets had been burnt opposite Friday Street in the previous reign. After the hats came a burning of fish panniers defective in measure; while in the reign of Edward III. some false chopins (wine measures) were destroyed. This was rough justice, but still the seizures seem to have been far fewer than they would be in our boastful epoch.
There was a generous lavishness about the royalty of the Middle Ages, however great a fool or scoundrel the monarch might be. Thus we read that on the safe delivery of Queen Isabel (wife of Edward II.), in 1312, of a son, afterwards Edward III., the Conduit in Chepe, for one day, ran with nothing but wine, for all those who chose to drink there; and at the cross, hard by the church of St. Michael in West Chepe, there was a pavilion extended in the middle of the street, in which was set a tun of wine, for all passers-by to drink of.
The mediæval guilds, useful as they were in keeping traders honest (Heaven knows, it needs supervision enough, now!), still gave rise to jealousies and feuds. The sturdy craftsmen of those days, inured to arms, flew to the sword as the quickest arbitrator, and preferred clubs and bills to Chancery courts and Common Pleas. The stones of Chepe were often crimsoned with the blood of these angry disputants. Thus, in 1327 (Edward III.), the saddlers and the joiners and bit-makers came to blows. In May of that year armed parties of these rival trades fought right and left in Cheapside and Cripplegate. The whole city ran to the windows in alarm, and several workmen were killed and many mortally wounded, to the great scandal of the City, and the peril of many quiet people. The conflict at last became so serious that the mayor, aldermen, and sheriffs had to interpose, and the dispute had to be finally settled at a great discussion of the three trades at the Guildhall, with what result the record does not state.
In this same reign of Edward III. the excessive length of the tavern signs ("ale-stakes" as they were then called) was complained of by persons riding in Cheapside. All the taverners of the City were therefore summoned to the Guildhall, and warned that no sign or bush (hence the proverb, "Good wine needs no bush") should henceforward extend over the king's highway beyond the length of seven feet, under pain of a fine of forty pence to the chamber of the Guildhall.
In 1340 (Edward III.) two more guilds fell to quarrelling. This time it was the pelterers (furriers) and fishmongers, who seem to have tanned each other's hides with considerable zeal. It came at last to this, that the portly mayor and sheriffs had to venture out among the sword-blades, cudgels, and whistling volleys of stones, but at first with little avail, for the combatants were too hot. They soon arrested some scaly and fluffy misdoers, it is true; but then came a wild rush, and the noisy misdoers were rescued; and, most audacious of all, one Thomas, son of John Hansard, fishmonger, with sword drawn (terrible to relate), seized the mayor by his august throat, and tried to lop him on the neck; and one brawny rascal, John le Brewere, a porter, desperately wounded one of the City serjeants: so that here, as the fishmongers would have observed, "there was a pretty kettle of fish." For striking a mayor blood for blood was the only expiation, and Thomas and John were at once tried at the Guildhall, found guilty on their own confession, and beheaded in Chepe; upon hearing which Edward III. wrote to the mayor, and complimented him on his display of energy on this occasion.
Chaucer speaks of the restless 'prentices of
Cheap (Edward III.):—
"A prentis dwelled whilom in our citee—
At every bridale would he sing and hoppe;
He loved bet the taverne than the shoppe—
For when ther eny riding was in Chepe
Out of the shoppe thider wold he lepe,
And til that he had all the sight ysein,
And danced wel, he wold not come agen."
(The Coke's Tale.)
In the luxurious reign of Richard II. the guilds were again vigilant, and set fire to a number of caps that had been oiled with rank grease, and that had been frilled by the feet and not by the hand, "so being false and made to deceive the commonalty." In this same reign (1393), when the air was growing dark with coming mischief, an ordinance was passed, prohibiting secret huckstering of stolen and bad goods by night "in the common hostels," instead of the two appointed markets held every feast-day, by daylight only, in Westchepe and Cornhill. The Westchepe market was held by day between St. Lawrence Lane and a house called "the Cage," between the first and second bell, and special provision was made that at these markets no crowd should obstruct the shops adjacent to the open-air market. To close the said markets the "bedel of the ward" was to ring a bell (probably, says Mr. Riley, the bell on the Tun, at Cornhill) twice—first, an hour before sunset, and another final one half an hour later. Another civic edict relating to markets occurs in 1379 (Richard II.), when the stands for stalls at the High Cross of Chepe were let by the mayor and chamberlain at 13s. 4d. each. At the same time the stalls round the brokers' cross, at the north door of St. Paul's (erected by the Earl of Gloucester in Henry III.'s reign) were let at 10s. and 6s. 8d. each. The stationers, or vendors in small wares, on the taking down of the Cross in 1390, probably retired to Paternoster Row.
The punishment of the pillory (either in Cheapside or Cornhill, the "Letter Book" does not say which) was freely used in the Middle Ages for scandal-mongers, dishonest traders, and forgers; and very deterring the shameful exposure must have been to even the most brazen offender. Thus, in Richard II.'s reign, we find John le Strattone, for obtaining thirteen marks by means of a forged letter, was led through Chepe with trumpets and pipes to the pillory on "Cornhalle" for one hour, on two successive days.
For the sake of classification we may here mention a few earlier instances of the same ignominious punishment. In 1372 (Edward III.) Nicholas Mollere, a smith's servant, for spreading a lying report that foreign merchants were to be allowed the same rights as freemen of the City, was set in the pillory for one hour, with a whetstone hung round his neck. In the same heroic reign Thomas Lanbye, a chapman, for selling rims of base metal for cups, pretending them to be silvergilt, was put in the pillory for two hours; while in 1382 (Richard II.) we find Roger Clerk, of Wandsworth, for pretending to cure a poor woman of fever by a talisman wrapped in cloth of gold, was ridden through the City to the music of trumpets and pipes; and the same year a cook in Bread Street, for selling stale slices of cooked conger, was put in the pillory for an hour, and the said fish burned under his rascally nose.
Sometimes, however, the punishment awarded to these civic offenders consisted in less disgraceful penance, as, for instance, in the year 1387 (Richard II.), a man named Highton, who had assaulted a worshipful alderman, was sentenced to lose his hand; but the man being a servant of the king, was begged off by certain lords, on condition of his walking through Chepe and Fleet Street, carrying a lighted wax candle of three pounds' weight to St. Dunstan's Church, where he was to offer it on the altar.
In 1591, the year Elizabeth sent her rash but brave young favourite, Essex, with 3,500 men, to help Henry IV. to besiege Rouen, two fanatics named Coppinger and Ardington, the former calling himself a prophet of mercy and the latter a prophet of vengeance, proclaimed their mission in Cheapside, and were at once laid by the heels. But the old public punishment still continued, for in 1600 (the year before the execution of Essex) we read that "Mrs. Fowler's case was decided" by sentencing that lady to be whipped in Bridewell; while a Captain Hermes was sent to the pillory, his brother was fined £100 and imprisoned, and Gascone, a soldier, was sentenced to ride to the Cheapside pillory with his face to the horse's tail, to be there branded in the face, and afterwards imprisoned for life.
In 1578, when Elizabeth was coquetting with Anjou and the French marriage, we find in one of those careful lists of the Papists of London kept by her subtle councillors, a Mr. Loe, vintner, of the "Mitre," Cheapside, who married Dr. Boner's sister (Bishop Bonner?). In 1587, the year before the defeat of the Armada, and when Leicester's army was still in Holland, doing little, and the very month that Sir William Stanley and 13,000 Englishmen surrendered Deventer to the Prince of Parma, we find the Council writing to the Lord Mayor about a mutiny, requiring him "to see that the soldiers levied in the City for service in the Low Countries, who had mutinied against Captain Sampson, be punished with some severe and extraordinary correction. To be tied to carts and flogged through Cheapside to Tower Hill, then to be set upon a pillory, and each to have one ear cut off."
In the reign of James I. the same ignominious and severe punishment continued, for in 1611 one Floyd (for we know not what offence) was fined £5,000, sentenced to be whipped to the pillories of Westminster and Cheapside, to be branded in the face, and then imprisoned in Newgate.
To return to our historical sequence. In 1388 (Richard II.) it was ordered that every person selling fish taken east of London Bridge should sell the same at the Cornhill market; while all Thames fish caught west of the bridge was to be sold near the conduit in Chepe, and nowhere else, under pain of forfeiture of the fish.
The eleventh year of Richard II. brought a real improvement to the growing city, for certain "substantial men of the ward of Farringdon Within" were then allowed to build a new water-conduit near the church of St. Michael le Quern, in Westchepe, to be supplied by the great pipe opposite St. Thomas of Accon, providing the great conduit should not be injured; and on this occasion the Earl of Gloucester's brokers' cross at St. Paul's was removed.
Early in the reign of Henry V. complaints were made by the poor that the brewers, who rented the fountains and chief upper pipe of the Cheapside conduit, also drew from the smaller pipe below, and the brewers were warned that for every future offence they would be fined 6s. 8d. In the fourth year of this chivalrous monarch a "hostiller" named Benedict Wolman, under-marshal of the Marshalsea, was condemned to death for a conspiracy to bring a man named Thomas Ward, alias Trumpington, from Scotland, to pass him off as Richard II. Wolman was drawn through Cornhill and Cheapside to the gallows at Tyburn, where he was "hanged and beheaded."
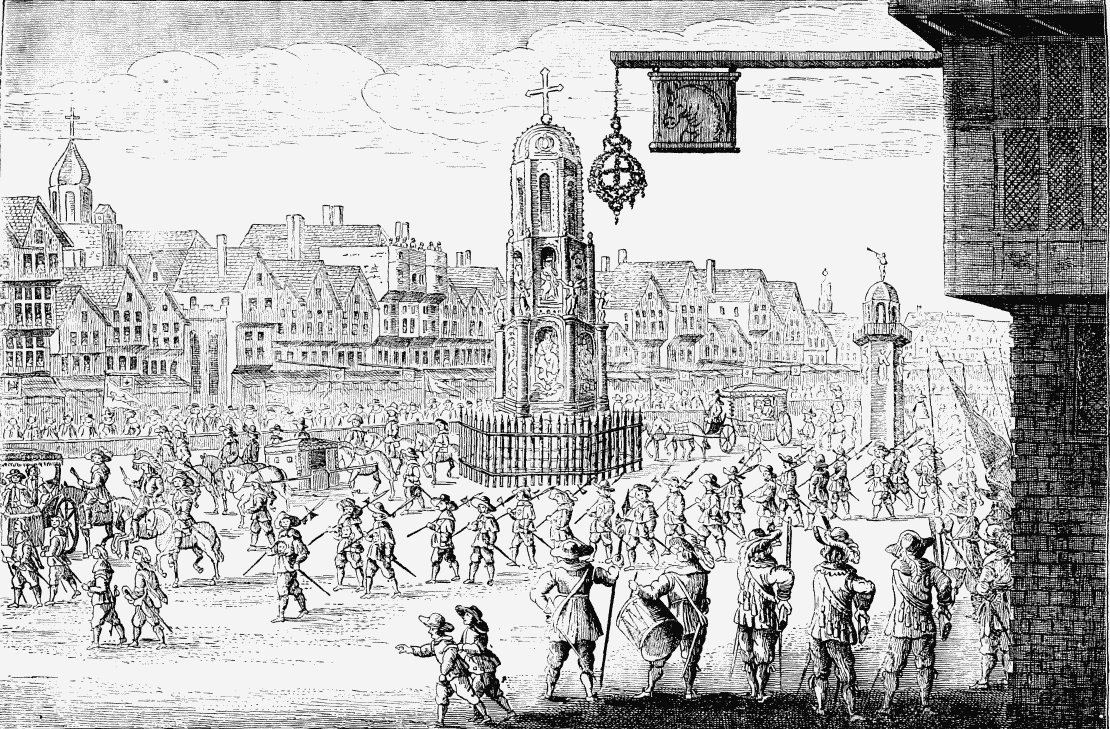
ANCIENT VIEW OF CHEAPSIDE. (From La Serre's "Entrée de la Revne Mère du Rov." showing the Procession of Mary de Medicis.)
Lydgate, that dull Suffolk monk, who followed
Chaucer, though at a great distance, has, in his
ballad of "Lackpenny," described Chepe in the
reign of Henry VI. The hero of the poem says—
"Then to the Chepe I gan me drawn,
Where much people I saw for to stand;
One offered me velvet, silk, and lawn;
Another he taketh me by the hand,
'Here is Paris thread, the finest in the land.'
I never was used to such things indeed,
And, wanting money, I might not speed."
In 1622 the traders of the Goldsmiths' Company began to complain that alien traders were creeping into and alloying the special haunts of the trade, Goldsmiths' Row and Lombard Street; and that 183 foreign goldsmiths were selling counterfeit jewels, engrossing the business and impoverishing its members.
City improvements were carried with a high hand in the reign of Charles I., who, determined to clear Cheapside of all but goldsmiths, in order to make the eastern approach to St. Paul's grander, committed to the Fleet some of the alien traders who refused to leave Cheapside. This unfortunate monarch seems to have carried out even his smaller measures in a despotic and unjustifiable manner, as we see from an entry in the State Papers, October 2, 1634. It is a petition of William Bankes, a Cheapside tavern-keeper, and deposes:—
"Petition of William Bankes to the king. Not fully twelve months since, petitioner having obtained a license under the Great Seal to draw wine and vent it at his house in Cheapside, and being scarce entered into his trade, it pleased his Majesty, taking into consideration the great disorders that grew by the numerous taverns within London, to stop so growing an evil by a total suppression of victuallers in Cheapside, &c., by which petitioner is much decayed in his fortune. Beseeches his Majesty to grant him (he not being of the Company of Vintners in London, but authorised merely by his Majesty) leave to victual and retail meat, it being a thing much desired by noblemen and gentlemen of the best rank and others (for the which, if they please, they may also contract beforehand, as the custom is in other countries), there being no other place fit for them to eat in the City."
The foolish determination to make Cheapside more glittering and showy seems again to have struck the weak despot, and an order of the Council (November 16) goes forth that—"Whereas in Goldsmith's Row, in Cheapside and Lombard Street, divers shops are held by persons of other trades, whereby that uniform show which was an ornament to those places and a justre to the City is now greatly diminished," all the shops in Goldsmith's Row are to be occupied by none but goldsmiths; and all the goldsmiths who keep shops in other parts of the City are to resort thither, or to Lombard Street or Cheapside."
The next year we find a tradesman who had been expelled from Goldsmiths' Row praying bitterly to be allowed a year longer, as he cannot find a residence, the removal of houses in Cheapside, Lombard Street, and St. Paul's Churchyard having rendered shops scarce.
In 1637 the king returns again to the charge, and determines to carry out his tyrannical whim by the following order of the Council:—"The Council threaten the Lord Mayor and aldermen with imprisonment, if they do not forthwith enforce the king's command that all shops should be shut up in Cheapside and Lombard Street that were not goldsmiths' shops." The Council "had learned that there were still twenty-four houses and shops that were not inhabited by goldsmiths, but in some of them were one Grove and Widow Hill, stationers; one Sanders, a drugster; Medcalfe, a cook; Renatus Edwards, a girdler; John Dover, a milliner; and Brown, a bandseller."
In 1664 we discover from a letter of the Dutch ambassador, Van Goch, to the States-General, that a great fire in Cheapside, "the principal street of the City," had burned six houses. In this reign the Cheapside market seems to have given great vexation to the Cheapside tradesmen. In 1665 there is a State Paper to this effect:—
"The inquest of Cheap, Cripplegate, Cordwainer, Bread Street, and Farringdon Within wards, to the Lord Mayor and Court of Aldermen of London. In spite of orders to the contrary, the abuses of Cheapside Market continue, and the streets are so pestered and encroached on that the passages are blocked up and trade decays. Request redress by fining those who allow stalls before their doors except at market times, or by appointing special persons to see to the matter, and disfranchise those who disobey; the offenders are 'marvellous obstinate and refractory to all good orders,' and not to be dealt with by common law."
Pepys, in his inimitable "Diary," gives us two interesting glimpses of Cheapside—one of the fermenting times immediately preceding the Restoration, the other a few years later—showing the effervescing spirit of the London 'prentices of Charles II.'s time:—
"1659.—Coming home, heard that in Cheapside there had been but a little before a gibbet set up, and the picture of Huson hung upon it in the middle of the street. (John Hewson, who had been a shoemaker, became a colonel in the Parliament army, and sat in judgment on the king. He escaped hanging by flight, and died in 1662 at Amsterdam.)
"1664.—So home, and in Cheapside, both coming and going, it was full of apprentices, who have been here all this day, and have done violence, I think, to the master of the boys that were put in the pillory yesterday. But Lord! to see how the trained-bands are raised upon this, the drums beating everywhere as if an enemy were upon them—so much is this city subject to be put into a disarray upon very small occasions. But it was pleasant to hear the boys, and particularly one very little one, that I demanded the business of. He told me that that had never been done in the City since it was a city—two 'prentices put in the pillory, and that it ought not to be so."
Cheapside has been the scene of two great riots, which were threatening enough to render them historically important. The one was in the reign of Richard I., the other in that of Henry VIII. The first of these, a violent protest against Norman oppression, was no doubt fomented, if not originated, by the down-trodden Saxons. It began thus:—On the return of Richard from his captivity in Germany, and before his fiery retaliation on France, a London citizen named William with the Long Beard (alias Fitzosbert, a deformed man, but of great courage and zeal for the poor), sought the king, and appealing to his better nature, laid before him a detail of great oppressions and outrages wrought by the Mayor and rich aldermen of the city, to burden the humbler citizens and relieve themselves, especially at "the hoistings" when any taxes or tollage were to be levied. Fitzosbert, encouraged at gaining the king's ear, and hoping too much from the generous but rapacious Norman soldier, grew bolder, openly defended the causes of oppressed men, and thus drew round him daily great crowds of the poor.
"Many gentlemen of honour," says Holinshed, "sore hated him for his presumptious attempts to the hindering of their purposes; but he had such comfort of the king that he little paused for their malice, but kept on his intent, till the king, being advertised of the assemblies which he made, commanded him to cease from such doings, that the people might fall again to their sciences and occupations, which they had for the most part left off at the instigation of this William with the Long Beard, which he nourished of purpose, to seem the more grave and manlike, and also, as it were, in despite of them which counterfeited the Normans (that were for the most part shaven), and because he would resemble the ancient usage of the English nation. The king's commandment in restraint of people's resort unto him was well kept for a time, but it was not long before they began to follow him again as they had done before. Then he took upon him to make unto them certain speeches. By these and such persuasions and means as he used, he had gotten two and fifty thousand persons ready to have taken his part."
How far this English Rienzi intended to obtain redress by force we cannot clearly discover; but he does not seem to have been a man who would have stopped at anything to obtain justice for the oppressed—and that the Normans were oppressors, till they became real Englishmen, there can be no doubt. The rich citizens and the Norman nobles, who had clamped the City fast with fortresses, soon barred out Longbeard from the king's chamber. The Archbishop of Canterbury especially, who ruled the City, called together the rich citizens, excited their fears, and with true priestly craft persuaded them to give sure pledges that no outbreak should take place, although he denied all belief in the possibility of such an event. The citizens, overcome by his oily and false words, willingly gave their pledges, and were from that time in the archbishop's power. The wily prelate then, finding the great demagogue was still followed by dangerous and threatening crowds, appointed two burgesses and other spies to watch Fitzosbert, and, when it was possible, to apprehend him.
These men at a convenient time set upon Fitzosbert, to bind and carry him off, but Longbeard was a hero at heart and full of ready courage. Snatching up an axe, he defended himself manfully, slew one of the archbishop's emissaries, and flew at once for sanctuary into the Church of St. Mary Bow. Barring the doors and retreating to the tower, he and some trusty friends turned it into a small fortress, till at last his enemies, gathering thicker round him and setting the steeple on fire, forced Longbeard and a woman whom he loved, and who had followed him there, into the open street.
As the deserted demagogue was dragged forth through the fire and smoke, still loth to yield, a son of the burgess whom he had stricken dead ran forward and stabbed him in the side. The wounded man was quickly overpowered, for the citizens, afraid to forfeit their pledges, did not come to his aid as he had expected, and he was hurried to the Tower, where the expectant archbishop sat ready to condemn him. We can imagine what that drum-head trial would be like. Longbeard was at once condemned, and with nine of his adherents, scorched and smoking from the fire, was sentenced to be hung on a gibbet at the Smithfield Elms. For all this, the fermentation did not soon subside; the people too late remembered how Fitzosbert had pleaded for their rights, and braved king, prelate, and baron; and they loudly exclaimed against the archbishop for breaking sanctuary, and putting to death a man who had only defended himself against assassins, and was innocent of other crimes. The love for the dead man, indeed, at last rose to such a height that the rumour ran that miracles were wrought by even touching the chains by which he had been bound in the Tower. He became for a time a saint to the poorer and more suffering subjects of the Normans, and the place where he was beheaded in Smithfield was visited as a spot of special holiness.
But this riot of Longbeard's was but the threatening of a storm. A tempest longer and more terrible broke over Cheapside on "Evil May Day," in the reign of Henry VIII. Its origin was the jealousy of the Lombards and other foreign money-lenders and craftsmen entertained by the artisans and 'prentices of London. Its actual cause was the seduction of a citizen's wife by a Lombard named Francis de Bard, of Lombard Street. The loss of the wife might have been borne, but the wife took with her, at the Italian's solicitation, a box of her husband's plate. The husband demanding first his wife and then his plate, was flatly refused both. The injured man tried the case at the Guildhall, but was foiled by the intriguing foreigner, who then had the incomparable rascality to arrest the poor man for his wife's board.
"This abuse," says Holinshed, "was much hated; so that the same and manie other oppressions done by the Lombards increased such a malice in the Englishmen's hearts, that at the last it burst out. For amongst others that sore grudged these matters was a broker in London, called John Lincolne, that busied himself so farre in the matter, that about Palme Sundie, in the eighth yeare of the King's reign, he came to one Doctor Henry Standish with these words: 'Sir, I understand that you shall preach at the Sanctuarie, Spittle, on Mondaie in Easter Weeke, and so it is, that Englishmen, both merchants and others, are undowne, for strangers have more liberty in this land than Englishmen, which is against all reason, and also against the commonweal of the realm. I beseech you, therefore, to declare this in your sermon, and in soe doing you shall deserve great thanks of my Lord Maior and of all his brethren;' and herewith he offered unto the said Doctor Standish a bill containing this matter more at large. . . Dr. Standish refused to have anything to do with the matter, and John Lincolne went to Dr. Bell, a chanon of the same Spittle, that was appointed likewise to preach upon the Tuesday in Easter Weeke, whome he perswaded to read his said bill in the pulpit."
This bill complained vehemently of the poverty of London artificers, who were starving, while the foreigners swarmed everywhere; also that the English merchants were impoverished by foreigners, who imported all silks, cloth of gold, wine, and iron, so that people scarcely cared even to buy of an Englishman. Moreover, the writer declared that foreigners had grown so numerous that, on a Sunday in the previous Lent, he had seen 600 strangers shooting together at the popinjay. He also insisted on the fact of the foreigners banding in fraternities, and clubbing together so large a fund, that they could overpower even the City of London.
Lincoln having won over Dr. Bell to read the complaint, went round and told every one he knew that shortly they would have news; and excited the 'prentices and artificers to expect some speedy rising against the foreign merchants and workmen. In due time the sermon was preached, and Dr. Bell drew a strong picture of the riches and indolence of the foreigners, and the struggling and poverty of English craftsmen.
The train was ready, and on such occasions the devil is never far away with the spark. The Sunday after the sermon, Francis de Bard, the aforesaid Lombard, and other foreign merchants, happened to be in the King's Gallery at Greenwich Palace, and were laughing and boasting over Bard's intrigue with the citizen's wife. Sir Thomas Palmer, to whom they spoke, said, "Sirs, you have too much favour in England;" and one William Bolt, a merchant, added, "Well, you Lombards, you rejoice now; but, by the masse, we will one day have a fling at you, come when it will." And that saying the other merchants affirmed. This tale was re ported about London.
The attack soon came. "On the 28th of April, 1513," says Holinshed, "some young citizens picked quarrels with the strangers, insulting them in various ways, in the streets; upon which certain of the said citizens were sent to prison. Then suddenly rose a secret rumour, and no one could tell how it began, that on May-day next the City would rise against the foreigners, and slay them; insomuch that several of the strangers fled from the City. This rumour reached the King's Council, and Cardinal Wolsey sent for the Mayor, to ask him what he knew of it; upon which the Mayor told him that peace should be kept. The Cardinal told him to take pains that it should be. The Mayor came from the Cardinal's at four in the afternoon of May-day eve, and in all haste sent for his brethren to the Guildhall; yet it was almost seven before they met. It was at last decided, with the consent of the Cardinal, that instead of a strong watch being set, which might irritate, all citizens should be warned to keep their servants within doors on the dreaded day. The Recorder and Sir Thomas More, of the King's Privy Council, came to the Guildhall, at a quarter to nine p.m., and desired the aldermen to send to every ward, forbidding citizen's servants to go out from seven p.m. that day to nine a.m. of the next day.
"After this command had been given," says the chronicler, "in the evening, as Sir John Mundie (an alderman) came from his ward, and found two young men in Chepe, playing at the bucklers, and a great many others looking on (for the command was then scarce known), he commanded them to leave off; and when one of them asked why, he would have had him to the counter. Then all the young 'prentices resisted the alderman, taking the young fellow from him, and crying ''Prentices and Clubs.' Then out of every door came clubs and weapons. The alderman fled, and was in great danger. Then more people arose out of every quarter, and forth came serving men, watermen, courtiers, and others; so that by eleven o'clock there were in Chepe six or seven hundred; and out of Paul's Churchyard came 300, which knew not of the other. So out of all places they gathered, and broke up the counters, and took out the prisoners that the Mayor had committed for hurting the strangers; and went to Newgate, and took out Studleie and Petit, committed thither for that cause.
"The Mayor and Sheriff made proclamation, but no heed was paid to them. Herewith being gathered in plumps, they ran through St. Nicholas' shambles, and at St. Martin's Gate there met with them Sir Thomas More, and others, desiring them to goe to their lodgings; and as they were thus intreating, and had almost persuaded the people to depart, they within St. Martin's threw out stones, bats, and hot water, so that they hurt divers honest persons that were there with Sir Thomas More; insomuch as at length one Nicholas Downes, a sergeant of arms, being there with the said Sir Thomas More, and sore hurt amongst others, cried 'Down with them!' and then all the misruled persons ran to the doors and windows of the houses round Saint Martin's, and spoiled all that they found.
"After that they ran headlong into Cornhill, and there likewise spoiled divers houses of the French men that dwelled within the gate of Master Newton's house, called Queene Gate. This Master Newton was a Picard borne, and reputed to be a great favourer of Frenchmen in their occupiengs and trades, contrary to the laws of the Citie. If the people had found him, they had surelie have stricken off his head; but when they found him not, the watermen and certain young preests that were there, fell to rifling, and some ran to Blanchapelton, and broke up the strangers' houses and spoiled them. Thus from ten or eleven of the clock these riotous people continued their outrageous doings, till about three of the clock, at what time they began to withdraw, and went to their places of resort; and by the way they were taken by the Maior and the heads of the Citie, and sent some of them to the Tower, some to Newgate, some to the counters, to the number of 300.
"Manie fled, and speciallie the watermen and preests and serving men, but the 'prentices were caught by the backs, and had to prison. In the meantime, whilst the hottest of this ruffling lasted, the Cardinall was advertised thereof by Sir Thomas Parre; whereon the Cardinall strengthened his house with men and ordnance. Sir Thomas Parre rode in all haste to Richmond, where the King lay, and informed him of the matter; who incontinentlie sent forth hastilie to London, to understand the state of the Citie, and was truely advertised how the riot had ceased, and manie of the misdoers apprehended. The Lieutenant of the Tower, Sir Roger Cholmeleie (no great friend to the Citie), in a frantike furie, during the time of this uprore, shot off certaine pieces of ordinance against the Citie, and though they did no great harm, yet he won much evil will for his hastie doing, because men thought he did it of malice, rather than of any discretion.
"About five o'clock, the Earls of Shrewsbury and Surrey, Thomas Dockerin, Lord of Saint John's George Neville, Lord of Abergavenny, came to London with such force as they could gather in haste, and so did the Innes of Court. Then were the prisoners examined, and the sermon of Dr. Bell brought to remembrance, and he sent to the Tower. Herewith was a Commission of Oyer and Determiner, directed to the Duke of Norfolk and other lords, to the Lord Mayor of London, and the aldermen, and to all the justices of England, for punishment of this insurrection. (The Citie thought the Duke bare them a grudge for a lewd preest of his that the yeare before was slaine in Chepe, insomuch that he then, in his fury, said, 'I pray God I may once have the citizens in my power!' And likewise the Duke thought that they bare him no good will; wherefore he came into the Citie with thirteen hundred men, in harnesse, to keepe the oier and determiner.)

BEGINNING OF THE RIOT IN CHEAPSIDE (see page 311).
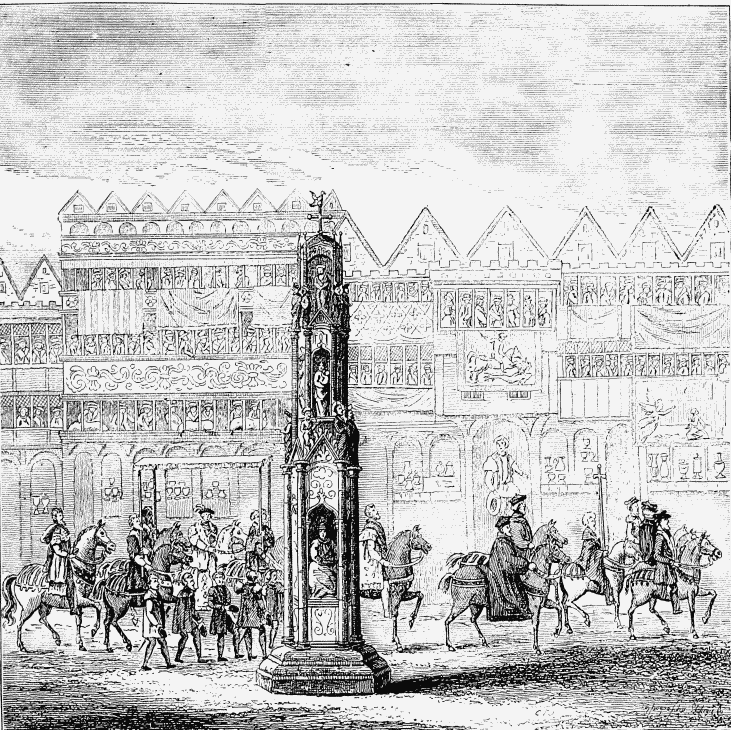
CHEAPSIDE CROSS, AS IT APPEARD IN 1547. (Showing part of the Procession of Edward VI. to his Coronation, from a Painting of the Time.)
"At the time of the examination the streets were filled with harnessed men, who spake very opprobrious words to the citizens, which the latter, although two hundred to one, bore patiently. The inquiry was held at the house of Sir John Fineux, Lord Chief Justice of England, neare to St. Bride's, in Fleet Street.
"When the lords were met at the Guildhall, the prisoners were brought through the street, tied in ropes, some men, and some lads of thirteen years of age. Among them were divers not of the City, some priests, some husbandmen and labourers. The whole number amounted unto two hundred, three score, and eighteen persons. Eventually, thirteen were found guilty, and adjudged to be hanged, drawn, and quartered. Eleven pairs of gallows were set up in various places where the offences had been committed, as at Aldgate, Blanchappleton, Gratious Street, Leaden Hall, and before every Counter. One also at Newgate, St. Martin's, at Aldersgate, and Bishopsgate. Then were the prisoners that were judged brought to those places of execution, and executed in the most rigorous manner in the presence of the Lord Edward Howard, son to the Duke of Norfolke, a knight marshal, who showed no mercic, but extreme crueltie to the poore yonglings in their execution; and likewise the duke's servants spake many opprobrious words. On Thursday, May the 7th, was Lincolne, Shirwin, and two brethren called Bets, and diverse other persons, adjudged to die; and Lincolne said, 'My lords, I meant well, for if you knew the mischiefe that is insued in this realme by strangers, you would remedie it. And many times I have complained, and then I was called a busie fellow; now, our Lord have mercie on me!' They were laid on hurdels and drawne to the Standard in Cheape, and first was John Lincolne executed; and as the others had the ropes about their neckes, there came a commandment from the king to respit the execution. Then the people cried, 'God save the king!' and so was the oier and terminer deferred till another daie, and the prisoners sent againe to ward. The armed men departed out of London, and all things set in quiet.
"On the 11th of May, the king being at Greenwich, the Recorder of London and several aldermen sought his presence to ask pardon for the late riot, and to beg for mercy for the prisoners; which petition the king sternly refused, saying that although it might be that the substantial citizens did not actually take part in the riot, it was evident, from their supineness in putting it down, that they 'winked at the matter.'
"On Thursday, the 22nd of May, the king, attended by the cardinal and many great lords, sat in person in judgment in Westminster Hall, the mayor, aldermen, and all the chief men of the City being present in their best livery. The king commanded that all the prisoners should be brought forth, so that in came the poore yonglings and old false knaves, bound in ropes, all along one after another in their shirts, and everie one a halter about his necke, to the number of now foure hundred men and eleven women; and when all were come before the king's presence, the cardinall sore laid to the maior and commonaltie their negligence; and to the prisoners he declared that they had deserved death for their offense. Then all the prisoners together cried, 'Mercie, gratious lord, mercie!' Herewith the lords altogither besought his grace of mercie, at whose sute the king pardoned them all. Then the cardinal gave unto them a good exhortation, to the great gladnesse of the hearers.
"Now when the generall pardon was pronounced all the prisoners shouted at once, and altogither cast up their halters into the hall roofe, so that the king might perceive they were none of the discreetest sort. Here is to be noticed that diverse offendors that were not taken, hearing that the king was inclined to mercie, came well apparelled to Westminster, and suddenlie stripped them into their shirts with halters, and came in among the prisoners, willinglie to be partakers of the king's pardon; by which dooing it was well known that one John Gelson, yeoman of the Crowne, was the first that began to spoile, and exhorted others to doe the same; and because he fled and was not taken, he came in with a rope among the other prisoners, and so had his pardon. This companie was after called the 'black-wagon.' Then were all the gallows within the Citie taken downe, and many a good prayer said for the king."
Jane Shore, that beautiful but frail woman, who married a goldsmith in Lombard Street, and was the mistress of Edward IV., was the daughter of a merchant in Cheapside. Drayton describes her minutely from a picture extant in Elizabeth's time, but now lost.
"Her stature," says the poet, "was meane; her haire of a dark yellow; her face round and full; her eye gray, delicate harmony being between each part's proportion and each proportion's colour; her body fat, white, and smooth; her countenance cheerful, and like to her condition. The picture I have seen of her was such as she rose out of her bed in the morning, having nothing on but a rich mantle cast under one arme over her shoulder, and sitting on a chair on which her naked arm did lie. Shore, a young man of right goodly person, wealth, and behaviour, abandoned her after the king had made her his concubine. Richard III., causing her to do open penance in St. Paul's Churchyard, commanded that no man should relieve her, which the tyrant did not so much for his hatred to sinne, but that, by making his brother's life odious, he might cover his horrible treasons the more cunningly."
An old ballad quaintly describes her supposed
death, following an entirely erroneous tradition:—
"My gowns, beset with pearl and gold,
Were turn'd to simple garments old;
My chains and gems, and golden rings,
To filthy rags and loathsome things.
"Thus was I scorned of maid and wife,
For leading such a wicked life;
Both sucking babes and children small,
Did make their pastime at my fall.
"I could not get one bit of bread,
Whereby my hunger might be fed,
Nor drink, but such as channels yield,
Or stinking ditches in the field.
"Thus weary of my life, at lengthe
I yielded up my vital strength,
Within a ditch of loathsome scent,
Where carrion dogs did much frequent;
"The which now, since my dying daye,
Is Shoreditch call'd, as writers saye; (fn. 1)
Which is a witness of my sinne,
For being concubine to a king."
Sir Thomas More, however, distinctly mentions Jane Shore being alive in the reign of Henry VIII., and seems to imply that he had himself seen her. "He(Richard III.) caused," says More, "the Bishop of London to put her to an open penance, going before the cross in procession upon a Sunday, with a taper in her hand; in which she went in countenance and face demure, so womanly, and albeit she were out of all array save her kirtle only, yet went she so fair and lovely, namely while the wondering of the people cast a comely red in her cheeks (of which she before had most miss), that her great shame was her much praise among those who were more amorous of her body than curious of her soul; and many good folk, also, who hated her living, and were glad to see sin corrected, yet pitied they more her penance than rejoiced therein, when they considered that the Protector procured it more of a corrupt intent than any virtuous intention.
"Proper she was, and fair; nothing in her body that you would have changed, but if you would, have wished her somewhat higher. Thus say they who knew her in her youth; albeit some who now see her (for yet she liveth) deem her never to have been well-visaged; whose judgment seemeth to me to be somewhat like as though men should guess the beauty of one long departed by her scalp taken out of the charnel-house. For now is she old, lean, withered, and dried up—nothing left but shrivelled skin and hard bone. And yet, being even such, whoso well advise her visage, might guess and devine which parts, how filled, would make it a fair face.
"Yet delighted men not so much in her beauty as in her pleasant behaviour. For a proper wit had she, and could both read well and write, merry in company, ready and quick of answer, neither mute nor full of babble, sometimes taunting without displeasure, and not without disport."