Old and New London: Volume 1. Originally published by Cassell, Petter & Galpin, London, 1878.
This free content was digitised by double rekeying. Public Domain.
Walter Thornbury, 'Temple Bar', in Old and New London: Volume 1(London, 1878), British History Online https://prod.british-history.ac.uk/old-new-london/vol1/pp22-31 [accessed 19 April 2025].
Walter Thornbury, 'Temple Bar', in Old and New London: Volume 1(London, 1878), British History Online, accessed April 19, 2025, https://prod.british-history.ac.uk/old-new-london/vol1/pp22-31.
Walter Thornbury. "Temple Bar". Old and New London: Volume 1. (London, 1878), British History Online. Web. 19 April 2025. https://prod.british-history.ac.uk/old-new-london/vol1/pp22-31.
In this section
CHAPTER II.
TEMPLE BAR.
Temple Bar—The Golgotha of English Traitors—When Temple Bar was made of Wood—Historical Pageants at Temple Bar—The Associations of Temple Bar—Mischievous Processions through Temple Bar—The First grim Trophy—Rye-House Plot Conspirators.
Temple Bar was rebuilt by Sir Christopher Wren, in 1670–72, soon after the Great Fire had swept away eighty-nine London churches, four out of the seven City gates, 460 streets, and 13,200 houses, and had destroyed fifteen of the twenty-six wards, and laid waste 436 acres of buildings, from the Tower eastward to the Inner Temple westward.
The old black gateway, once the dreaded Golgotha of English traitors, separates, it should be remembered, the Strand from Fleet Street, the city from the shire, and the Freedom of the City of London from the Liberty of the City of Westminster. As Hatton (1708—Queen Anne) says,—"This gate opens not immediately into the City itself, but into the Liberty or Freedom thereof." We need hardly say that nothing can be more erroneous than the ordinary London supposition that Temple Bar ever formed part of the City fortifications. Mr. Gilbert à Beckett, laughing at this tradition, once said in Punch: "Temple Bar has always seemed to me a weak point in the fortifications of London. Bless you, the besieging army would never stay to bombard it—they would dash through the barber's."
The Great Fire never reached nearer Temple Bar than the Inner Temple, on the south side of Fleet Steet, and St. Dunstan's Church, on the north.
The Bar is of Portland stone, which London smoke alternately blackens and calcines; and each façade has four Corinthian pilasters, an entablature, and an arched pediment. On the west (Strand) side, in two niches, stand, as eternal sentries, Charles I. and Charles II., in Roman costume. Charles I. has long ago lost his bâton, as he once deliberately lost his head. Over the keystone of the central arch there used to be the royal arms. On the east side are James I. and Elizabeth (by many able writers supposed to be Anne of Denmark, James I.'s queen). She is pointing her white finger at Child's; while he, looking down on the passing cabs, seems to say, "I am nearly tired of standing; suppose we go to Whitehall, and sit down a bit?"
The slab over the eastern side of the arch bears the following inscription, now all but smoothed down by time:—
"Erected in the year 1670, Sir Samuel Starling, Mayor; continued in the year 1671, Sir Richard Ford, Lord Mayor; and finished in the year, 1672, Sir George Waterman, Lord Mayor."
All these persons were friends of Pepys.
The upper part of the Bar is flanked by scrolls, but the fruit and flowers once sculptured on the pediment, and the supporters of the royal arms over the posterns, have crumbled away. In the centre of each façade is a semicircular-headed, ecclesiastical-looking window, that casts a dim horny light into a room above the gate, held of the City, at an annual rent of some £50, by Messrs. Childs, the bankers, as a sort of muniment-room for their old account-books. There is here preserved, among other costlier treasures of Mammon, the private account-book of Charles II. The original Child was a friend of Pepys, and is mentioned by him as quarrelling with the Duke of York on Admiralty matters. The Child who succeeded him was a friend of Pope, and all but led him into the South-Sea Bubble speculation.
Those affected, mean statues, with the crinkly drapery, were the work of a vain, half-crazed sculptor named John Bushnell, who died mad in 1701. Bushnell, who had visited Rome and Venice, executed Cowley's monument in Westminster Abbey, and the statues of Charles I., Charles II., and Gresham, in the Old Exchange.
There is no extant historical account of Temple Bar in which the following passage from Strype (George I.) is not to be found embedded like a fossil; it is, in fact, nearly all we London topographers know of the early history of the Bar:— "Anciently," says Strype, "there were only posts, rails, and a chain, such as are now in Holborn, Smithfield, and Whitechapel bars. Afterwards there was a house of timber erected across the street, with a narrow gateway and an entry on the south side of it under the house." This structure is to be seen in the bird's-eye view of London, 1601 (Elizabeth), and in Hollar's seven-sheet map of London (Charles II.)
The date of the erection of the "wooden house" is not to be ascertained; but there is the house plain enough in a view of London to which Maitland affixes the date about 1560 (the second year of Elizabeth), so we may perhaps safely put it down as early as Edward VI. or Henry VIII. Indeed, if a certain scrap of history is correct—i.e., that bluff King Hal once threatened, if a certain Bill did not pass the Commons a little quicker, to fix the heads of several refractory M.P.s on the top of Temple Bar—we must suppose the old City toll-gate to be as old as the early Tudors.
After Simon de Montfort's death, at the battle of Evesham, 1265, Prince Edward, afterwards Edward I., punished the rebellious Londoners, who had befriended Montfort, by taking away all their street chains and bars, and locking them up in the Tower.
The earliest known documentary and historical notice of Temple Bar is in 1327, the first year of Edward III.; and in the thirty-fourth year of the same reign we find, at an inquisition before the mayor, twelve witnesses deposing that the commonalty of the City had, time out of mind, had free ingress and egress from the City to Thames and from Thames to the City, through the great gate of the Templars situate within Temple Bar. This referred to some dispute about the right of way through the Temple, built in the reign of Henry I. In 1384 Richard II. granted a licence for paving Strand Street from Temple Bar to the Savoy, and collecting tolls to cover such charges.
The historical pageants that have taken place at Temple Bar deserve a notice, however short. On the 5th of November, 1422, the corpse of that brave and chivalrous king, the hero of Agincourt, Henry V., was borne to its rest at Westminster Abbey by the chief citizens and nobles, and every doorway from Southwark to Temple Bar had its mournful torch-bearer. In 1502–3 the hearse of Elizabeth of York, queen of Henry VII., halted at Temple Bar, on its way from the Tower to Westminster, and at the Bar the Abbots of Westminster and Bermondsey blessed the corpse, and the Earl of Derby and a large company of nobles joined the sable funeral throng. After sorrow came joy, and after joy sorrow—Ita vita. In the next reign poor Anne Boleyn, radiant with happiness and triumph, came through the Bar (May 31, 1534), on her way to the Tower, to be welcomed by the clamorous citizens, the day before her ill-starred coronation. Temple Bar on that occasion was new painted and repaired, and near it stood singing men and children—the Fleet Street conduit all the time running claret. The old gate figures more conspicuously the day before the coronation of that wondrous child, Edward VI. Two hogsheads of wine were then ladled out to the thirsty mob, and the gate at Temple Bar was painted with battlements and buttresses, richly hung with cloth of Arras, and all in a flutter with "fourteen standard flags." There were eight French trumpeters blowing their best, besides "a pair of regals," with children singing to the same. In September, 1553, when Edward's cold-hearted half-sister, Mary Tudor, came through the City, according to ancient English custom, the day before her coronation, she did not ride on horseback, as Edward had done, but sat in a chariot covered with cloth of tissue and drawn by six horses draped with the same. Minstrels piped and trumpeted at Ludgate, and Temple Bar was newly painted and hung.
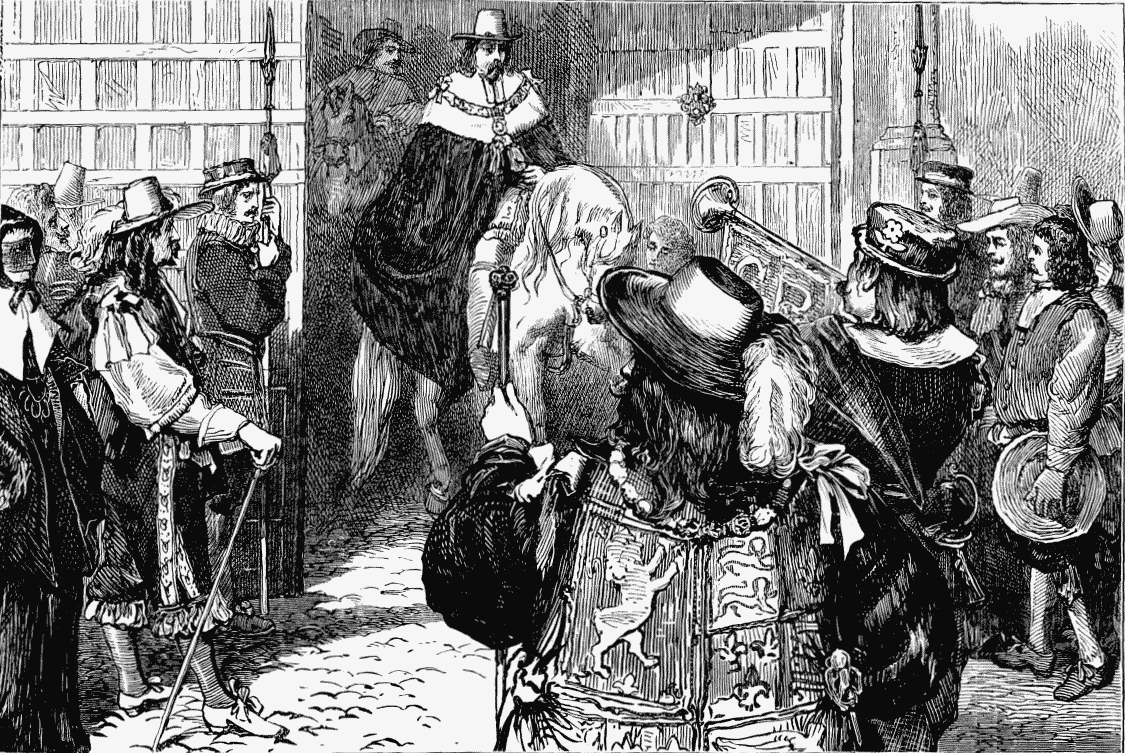
Proclamation of Charles II. at Temple Bar (see page 26).
Old Temple Bar, the background to many historical scenes, figures in the rash rebellion of Sir Thomas Wyatt. When he had fought his way down Piccadilly to the Strand, Temple Bar was thrown open to him, or forced open by him; but when he had been repulsed at Ludgate he was hemmed in by cavalry at Temple Bar, where he surrendered. This foolish revolt led to the death of innocent Lady Jane Grey, and brought sixty brave gentlemen to the scaffold and the gallows.

Penance of the Duchess of Gloucester (see page 32).
On Elizabeth's procession from the Tower before her coronation, January, 1559, Gogmagog the Albion, and Corineus the Briton, the two Guildhall giants, stood on the Bar; and on the south side there were chorister lads, one of whom, richly attired as a page, bade the queen farewell in the name of the whole City. In 1588, the glorious year that the Armada was defeated, Elizabeth passed through the Bar on her way to return thanks to God solemnly at St. Paul's. The City waits stood in triumph on the roof of the gate. The Lord Mayor and Aldermen, in scarlet gowns, welcomed the queen and delivered up the City sword, then on her return they took horse and rode before her. The City Companies lined the north side of the street, the lawyers and gentlemen of the Inns of Court the south. Among the latter stood a person afterwards not altogether unknown, one Francis Bacon, who displayed his wit by saying to a friend, "Mark the courtiers! Those who bow first to the citizens are in debt; those who bow first to us are at law!"
In 1601, when the Earl of Essex made his insane attempt to rouse the City to rebellion, Temple Bar, we are told, was thrown open to him; but Ludgate being closed against him on his retreat from Cheapside, he came back by boat to Essex House, where he surrendered after a short and useless resistance.
King James made his first public entry into his royal City of London, with his consort and son Henry, upon the 15th of March, 1603–4. The king was mounted upon a white genet, ambling through the crowded streets under a canopy held by eight gentlemen of the Privy Chamber, as representatives of the Barons of the Cinque Ports, and passed under six arches of triumph, to take his leave at the Temple of Janus, erected for the occasion at Temple Bar. This edifice was fiftyseven feet high, proportioned in every respect like a temple.
In June, 1649 (the year of the execution of Charles), Cromwell and the Parliament dined at Guildhall in state, and the mayor, says Whitelocke, delivered up the sword to the Speaker, at Temple Bar, as he had before done to King Charles.
Philips, Milton's nephew, who wrote the continuation of Baker's Chronicle, describes the ceremony at Temple Bar on the proclamation of Charles II. The old oak gates being shut, the king-at-arms, with tabard on and trumpet before him, knocked and gravely demanded entrance. The Lord Mayor appointed some one to ask who knocked. The king-at-arms replied, that if they would open the wicket, and let the Lord Mayor come thither, he would to him deliver his message. The Lord Mayor then appeared, tremendous in crimson velvet gown, and on horseback, of all things in the world, the trumpets sounding as the gallant knight pricked forth to demand of the herald, who he was and what was his message. The bold herald, with his hat on, answered, regardless of Lindley Murray, who was yet unknown, "We are the herald-at-arms appointed and commanded by the Lords and Commons assembled in Parliament, and demand an entrance into the famous City of London, to proclaim Charles II. King of England, Scotland, France, and Ireland, and we expect your speedy answer to our demand." An alderman then replied, "The message is accepted," and the gates were thrown open.
When William III. came to see the City and the Lord Mayor's Show in 1689, the City militia, holding lighted flambeaux, lined Fleet Street as far as Temple Bar.
The shadow of every monarch and popular hero since Charles II.'s time has rested for at least a passing moment at the old gateway. Queen Anne passed here to return thanks at St. Paul's for the victory of Blenheim. Here Marlborough's coach ominously broke down in 1714, when he returned in triumph from his voluntary exile.
George III. passed through Temple Bar, young and happy, the year after his coronation, and again when, old and almost broken-hearted, he returned thanks for his partial recovery from insanity; and in our time that graceless son of his, the Prince Regent, came through the Bar in 1814, to thank God at St. Paul's for the downfall of Bonaparte.
On the 9th November, 1837, the accession of Queen Victoria, Sir Peter Laurie, picturesque in scarlet gown, Spanish hat, and black feathers, presented the City sword to the Queen at Temple Bar; Sir Peter was again ready with the same weapon in 1844, when the Queen opened the new Royal Exchange; but in 1851, when her Majesty once more visited the City, the old ceremony was (wrongly, we think) dispensed with.
At the funeral of Lord Nelson, the honoured corpse, followed by downcast old sailors, was met at the Bar by the Lord Mayor and the Corporation; and the Great Duke's funeral car, and the long train of representative soldiers, rested at the Bar, which was hung with black velvet.
A few earlier associations connected with the present Bar deserve a moment or two's recollection. On February 12th, when General Monk—"Honest George," as his old Cromwellian soldiers used to call him—entered London, dislodged the "Rump" Parliament, and prepared for the Restoration of Charles II., bonfires were lit, the City bells rung, and London broke into a sudden flame of joy. Pepys, walking homeward about ten o'clock, says:— "The common joy was everywhere to be seen. The number of bonfires—there being fourteen between St. Dunstan's and Temple Bar, and at Strand Bridge, east of Catherine Street, I could at one time tell thirty-one fires."
On November 17, 1679, the year after the sham Popish Plot concocted by those matchless scoundrels, Titus Oates, an expelled naval. chaplain, and Bedloe; a swindler and thief, Temple Bar was made the spot for a great mob pilgrimage, on the anniversary of the accession of Queen Elizabeth, The ceremonial is supposed to have been organised by that restless plotter against a Popish succession, Lord Shaftesbury, and the gentlemen of the Green Ribbon Club, whose tavern, the "King's Head," was at the corner of Chancery Lane, opposite the Inner Temple gate. To scare and vex the Papists, the church bells began to clash out as early as three o'clock on the morning of that dangerous day. At dusk the procession of several thousand half-crazed torch-bearers started from Moorgate, along Bishopsgate Street, and down Houndsditch and Aldgate (passing Shaftesbury's house imagine the roar of the monster mob, the wave of torches, and the fiery fountains of squibs at that point!), then through Leadenhall Street and Cornhill, by the Royal Exchange, along Cheapside and on to Temple Bar, where the bonfire awaited the puppets. In a torrent of fire the noisy Protestants passed through the exulting City, making the Papists cower and shudder in their garrets and cellars, and before the flaming deluge opened a storm of shouting people. This procession consisted of fifteen groups of priests, Jesuits, and friars, two following a man on a horse, holding up before him a dummy, dressed to represent Sir Edmondbury Godfrey, a Protestant justice and wood merchant, supposed to have been murdered by Roman Catholics at Somerset House. It was attended by a body-guard of 150 swordbearers and a man roaring a political cry of the time through a brazen speaking-trumpet. The great bonfire was built up mountain high opposite the Inner Temple gate. Some zealous Protestants, by pre-arrangement, had crowned the prim and meagre statue of Elizabeth (still on the east side of the Bar) with a wreath of gilt laurel, and placed under her hand (that now points to Child's Bank) a golden glistening shield, with the motto, "The Protestant Religion and Magna Charta," inscribed upon it. Several lighted torches were stuck before her niche. Lastly, amidst a fiery shower of squibs from every door and window, the Pope and his companions were toppled into the huge bonfire, with shouts that reached almost to Charing Cross.
These mischievous processions were continued till the reign of George I. There was to have been a magnificent one on November 17, 1711, when the Whigs were dreading the contemplated peace with the French and the return of Marlborough. But the Tories, declaring that the Kit-Cat Club was urging the mob to destroy the house of Harley, the Minister, and to tear him to pieces, seized on the wax figures in Drury Lane, and forbade the ceremony.
As early as two years after the Restoration, Sir Balthazar Gerbier, a restless architectural quack and adventurer of those days, wrote a pamphlet proposing a sumptuous gate at Temple Bar, and the levelling of the Fleet Valley. After the Great Fire Charles II. himself hurried the erection of the Bar, and promised money to carry out the work. During the Great Fire, Temple Bar was one of the stations for constables, 100 firemen, and 30 soldiers.
The Rye-House Plot brought the first trophy to the Golgotha of the Bar, in 1684, twelve years after its erection. Sir Thomas Armstrong was deep in the scheme. If the discreditable witnesses examined against Lord William Russell are to be believed, a plot had been concocted by a few desperate men to assassinate "the Blackbird and the Goldfinch "—as the conspirators called the King and the Duke of York—as they were in their coach on their way from Newmarket to London. This plan seems to have been the suggestion of Rumbold, a maltster, who lived in a lonely moated farmhouse, called Rye House, about eighteen miles from London, near the river Ware, close to a by-road that leads from Bishop Stortford to Hoddesdon. Charles II. had a violent hatred to Armstrong, who had been his Gentleman of the Horse, and was supposed to have incited his illegitimate son, the Duke of Monmouth, to rebellion. Sir Thomas was hanged at Tyburn. After the body had hung half an hour, the hangman cut it down, stripped it, lopped off the head, threw the heart into a fire, and divided, the body into four parts. The fore-quarter (afterbeing boiled in pitch at Newgate) was set on Temple Bar, the head was placed on Westminster Hall, and the rest of the body was sent to Stafford, which town Sir Thomas represented in Parliament.
Eleven years after, the heads of two more traitors —this time conspirators against William III.— joined the relic of Armstrong. Sir John Friend was a rich brewer at Aldgate. Parkyns was an old Warwickshire county gentleman. The plotters had several plans. One was to attack Kensington Palace at night, scale the outer wall, and storm or fire the building; another was to kill William on a Sunday, as he drove from Kensington to the chapel at St. James's Palace. The murderers agreed to assemble near where Apsley House now standsJust as the royal coach passed from Hyde Park across to the Green Park, thirty conspirators agreed to fall on the twenty-five guards, and butcher the king before he could leap out of his carriageThese two Jacobite gentlemen died bravely, proclaiming their entire loyalty to King James and the "Prince of Wales."
The unfortunate gentlemen who took a moody pleasure in drinking "the squeezing of the rotten Orange" had long passed on their doleful journey from Newgate to Tyburn before the ghastly procession of the brave and unlucky men of the rising, in 1715 began its mournful march. (fn. 1)
Sir Bernard Burke mentions a tradition that the head of the young Earl of Derwentwater was exposed on Temple Bar in 1716, and that his wife drove in a cart under the arch while a man hired, for the purpose threw down to her the beloved head from the parapet above. But the story is entirely untrue, and is only a version of the way in which the head of Sir Thomas More was removed by his son-in-law and daughter from London Bridge, where that cruel tyrant Henry VIII. had placed it. Some years ago, when the Earl of Derwentwater's coffin was found in the family vault, the head was lying safe with the body. In 1716 there was, however, a traitor's head spiked on the Bar—that of Colonel John Oxburgh, the victim of mistaken fidelity to a bad cause. He was a brave Lancashire gentleman, who had surrendered with his forces at Preston. He displayed signal courage and resignation in prison, forgetting himself to comfort others.
The next victim was Mr. Christopher Layer, a young Norfolk man and a Jacobite barrister, living in Southampton Buildings, Chancery Lane. He plunged deeply into the Atterbury Plot of 1722, and, with Lords North and Grey, enlisted men, hired officers, and, taking advantage of the universal misery caused by the bursting 'of the South Sea Bubble, planned a general rising against George I. The scheme was, with four distinct bodies of Jacobites, to seize the Tower and the Bank, to arrest the king and the prince, and capture or kill Lord Cadogan, one of the Ministers. At the trial it was proved that Layer had been over to Rome, and had seen the Pretender, who, by proxy, had stood godfather to his child. Troops were to be sent from France; barricades were to be thrown up all over London. The Jacobites had calculated that the Government had only 14,000 men to meet them— 3,000 of these would be wanted to guard London, 3,000 for Scotland, and 2,000 for the garrisons. The original design had been to take advantage of the king's departure for Hanover, and, in the words of one of the conspirators, the Jacobites were fully convinced that "they should walk King George out before Lady-day." Layer was hanged at Tyburn, and his head fixed upon Temple Bar.
Years after, one stormy night in 1753, the rebel's skull blew down, and was picked up by a nonjuring attorney, named Pierce, who preserved it as a relic of the Jacobite martyr. It is said that Dr. Richard Rawlinson, an eminent antiquary, obtained what he thought was Layer's head, and desired in his will that it should be placed in his right hand when he was buried. Another version of the story is, that a spurious skull was foisted upon Rawlinson, who died happy in the possession of the doubtful treasure. Rawlinson was bantered by Addison for his pedantry, in one of the Tatlers, and was praised by Dr. Johnson for his learning.
The 1745 rebellion brought the heads of fresh victims to the Bar, and this was the last triumph of barbarous justice. Colonel Francis Townley's was the sixth head; Fletcher's (his fellow-officer), the seventh and last. The Earls of Kilmarnock and Cromarty, Lord Balmerino, and thirty-seven other rebels (thirty-six of them having been captured in Carlisle) were tried the same session. Townley was a man of about fifty-four years of age, nephew of Mr. Townley of Townley Hall, in Lancashire (the "Townley Marbles" family), who had been tried and acquitted in 1725, though many of his men were found guilty and executed. The nephew had gone over to France in 1727, and obtained a commission from the French king, whom he served for fifteen years, being at the siege of Philipsburg, and close to the Duke of Berwick when that general's head was shot off. About 1740, Townley stole over to, England to see his friends and to plot against the Hanover family; and as soon as the rebels came into England, he met them between Lancaster and Preston, and came with them to Manchester. At the trial Roger M'Donald, an officer's servant, deposed to seeing Townley on the retreat from Derby, and between Lancaster and Preston riding at the head of the Manchester regiment on a bay horse. He had a white cockade in his hat and wore a plaid sash.
George Fletcher, who was tried at the same time as Townley, was a rash young chapman, who managed his widowed mother's provision shop "at Salford, just over the bridge in Manchester." His mother had begged him on her knees to keep out of the rebellion, even offering him a thousand pounds for his own pocket, if he would stay at home. He bought a captain's commission of Murray, the Pretender's secretary, for fifty pounds; wore the smart white cockade and a Highland plaid sash lined with white silk; and headed the very first captain's guard mounted for the Pretender at Carlisle. A Manchester man deposed to seeing at the Exchange a sergeant, with a drum, beating up for volunteers for the Manchester regiment.
Fletcher, Townley, and seven other unfortunate Jacobites were hanged on Kennington Common. Before the carts drove away, the men flung their prayer-books, written speeches, and gold-laced hats gaily to the crowd. Mr. James (Jemmy) Dawson, the hero of Shenstone's touching ballad, was one of the nine. As soon as they were dead the hangman cut down the bodies, disembowelled, beheaded, and quartered them, throwing the hearts into the fire. A monster—a fighting-man of the day, named Buckhorse—is said to have actually eaten a piece of Townley's flesh, to show his loyalty. Before the ghastly scene was over, the heart of one unhappy spectator had already broken. The lady to whom James Dawson was engaged to be married followed the rebels to the common, and even came near enough to see, with pallid face, the fire kindling, the axe, the coffins, and all the other dreadful preparations. She bore up bravely, until she heard her lover was no more. Then she drew her head back into the coach, and crying out, "My dear, I follow thee—I follow thee! Lord God, receive our souls, I pray Thee!" fell on the neck of a companion and expired. Mr. Dawson had behaved gallantly in prison, saying, "He did not care if they put a ton weight of iron upon him, it would not daunt him."
A curious old print of 1746, full of vulgar triumph,
reproduces a "Temple Bar, the City Golgotha," representing the Bar with three heads on the top of it,
spiked on long iron rods. The devil looks down
in ribald triumph from above, and waves a rebel
banner, on which, besides three coffins and a crown,
is the motto, "A crown or a grave." Underneath
are written these patriotic but doggrel lines:—
"Observe the banner which would all enslave,
Which misled traytors did so proudly wave;
The devil seems the project to surprise;
A fiend confused from off the trophy flies.
While trembling rebels at the fabric gaze,
And dread their fate with horror and amaze,
Let Britain's sons the emblematic view,
And plainly see what is rebellion's due."
The heads of Fletcher and Townley were put on the Bar August 12, 1746. On August 15th Horace Walpole, writing to a friend, says he had just been roaming in the City, and "passed under the new heads on Temple Bar, where people make a trade of letting spy-glasses at a halfpenny a look." According to Mr. J. T. Smith, an old man living in 1825 remembered, the last heads on Temple Bar being visible through a telescope across the space between the Bar and Leicester Fields.
Between two and three A.M., on the morning of January 20, 1766, a mysterious man was arrested by the watch as he was discharging, by the dim light, musket bullets at the two heads then remaining upon Temple Bar. On being questioned by the puzzled magistrate, he affected a disorder in his senses, and craftily declared that the patriotic reason for his eccentric conduct was his strong attachment to the present Government, and that he thought it not sufficient that a traitor should merely suffer death; that this provoked his indignation, and it had been his constant practice for three nights past to amuse himself in the same manner. "And it is much to be feared," says the past record of the event, "that the man is a near relation to one of the unhappy sufferers." Upon searching this very suspicious marksman, about fifty musket bullets were found on him, wrapped up in a paper on which was written the motto, "Eripuit ille vitam."
After this, history leaves the heads of the unhappy
Jacobites—those lips that love had kissed, those:
cheeks children had patted—to moulder on in the
sun and in the rain, till the last day of March, 1772,.
when one of them (Townley or Fletcher) fell. The
last stormy gust of March threw it down, and a
short time after a strong wind blew down the other;
and against the sky no more relics remained of
a barbarous and unchristian revenge. In April,
1773, Boswell, whom we all despise and all like,.
dined at courtly Mr. Beauclerk's with Dr. Johnson,
Lord Charlemont (Hogarth's friend), Sir Joshua
Reynolds, and other members of the literaryclub, in Gerrard Street, Soho, it being the awful
evening when Boswell was to be balloted forThe conversation turned on the new and commendable practice of erecting monuments to great
men in St. Paul's. The Doctor observed: "I remember once being with Goldsmith in Westminster
Abbey. Whilst we stood at Poet's Corner, I said
to him,—
"Forsitan et nostrum nomen miscebitur istis."—Ovid.
When we got to Temple Bar he stopped me, and
pointing to the heads upon it, slily whispered,—
"Forsitan et nostrum nomen miscebitur istis."
This anecdote, so full of clever, arch wit, is sufficient
to endear the old gateway to all lovers of Johnson
and of Goldsmith.
According to Mr. Timbs, in his "London and Westminster," Mrs. Black, the wife of the editor of the Morning Chronicle, when asked if she remembered any heads on Temple Bar, used to reply, in her brusque, hearty way, "Boys, I recollect the scene well! I have seen on that Temple Bar, about which you ask, two human heads—real heads— traitors' heads—spiked on iron poles. There were two; I saw one fall (March 31, 1772). . Women shrieked as it fell; men, as I have heard, shrieked. One woman near me fainted. Yes, boys, I recollect seeing human heads upon Temple Bar."
The cruel-looking spikes were removed early in the present century. The panelled oak gates have often been renewed, though certainly shutting them too often never wore them out.
As early as 1790 Alderman Pickett (who built the St. Clement's arch), with other subversive reformers, tried to pull down Temple Bar. It was pronounced unworthy of form, of no antiquity, an ambuscade for pickpockets, and a record of only the dark and crimson pages of history.
A writer in the Gentleman's Magazine, in 1813; chronicling the clearance away of some hovels encroaching upon the building, says: "It will not be surprising if certain amateurs, busy in improving the architectural concerns of the City, should at length request of their brethren to allow the Bar or grand gate of entrance into the City of London to stand, after they have so repeatedly sought to obtain its destruction." In 1852 a proposal for its repair and restoration was defeated in the Common Council; and twelve months later, a number of bankers, merchants, and traders set their hands to a petition for its removal altogether, as serving no practical purpose, as it impeded ventilation and retarded improvements. Since then Mr. Heywood has proposed to make a circus at Temple Bar, leaving the archway in the centre; and Mr. W. Burges, the architect, suggested a new arch in keeping with the new Law Courts opposite.

The room over Temple Bar (see page 37).
It is a singular fact that the "Parentalia," a chronicle of Wren's works written by Wren's clever son, contains hardly anything about Temple Bar. According to Mr Noble, the Wren manuscripts in the British Museum, Wren's ledger in the Bodleian, and the Record Office documents, are equally silent; but from a folio at the Guildhall, entitled "Expenses of Public Buildings after the Great Fire," it would appear that the Bar cost altogether £1,397 10s.; Bushnell, the sculptor, receiving out of this sum £480 for his four stone monarchs. The mason was John Marshall, who carved the pedestal of the statue of Charles I. at Charing Cross and worked on the Monument in Fish Street Hill. In 1636 Inigo Jones had designed a new arch, the plan of which still exists. Wren, it is said, took his design of the Bar from an old temple at Rome.
The old Bar is now a mere piece of useless and disused armour. Once a protection, then an ornament, it has now become an obstruction—the too narrow neck of a large decanter—a bone in the throat of Fleet Street. Yet still we have a lingering fondness for the old barrier that we have seen draped in black for a dead hero and glittering with gold in honour of a young bride. We have shared the sunshine that brightened it and the gloom that has darkened it, and we feel for it a species of friendship, in which it mutely shares. To us there seems to be a dignity in its dirt and pathos in the mud that bespatters its patient old face, as, like a sturdy fortress, it holds out against all its enemies, and Charles I. and II., and Elizabeth and James I. keep a bright look-out day and night for all attacks. Nevertheless, it must go in time, we fear. Poor old Temple Bar, we shall miss you when you are gone!
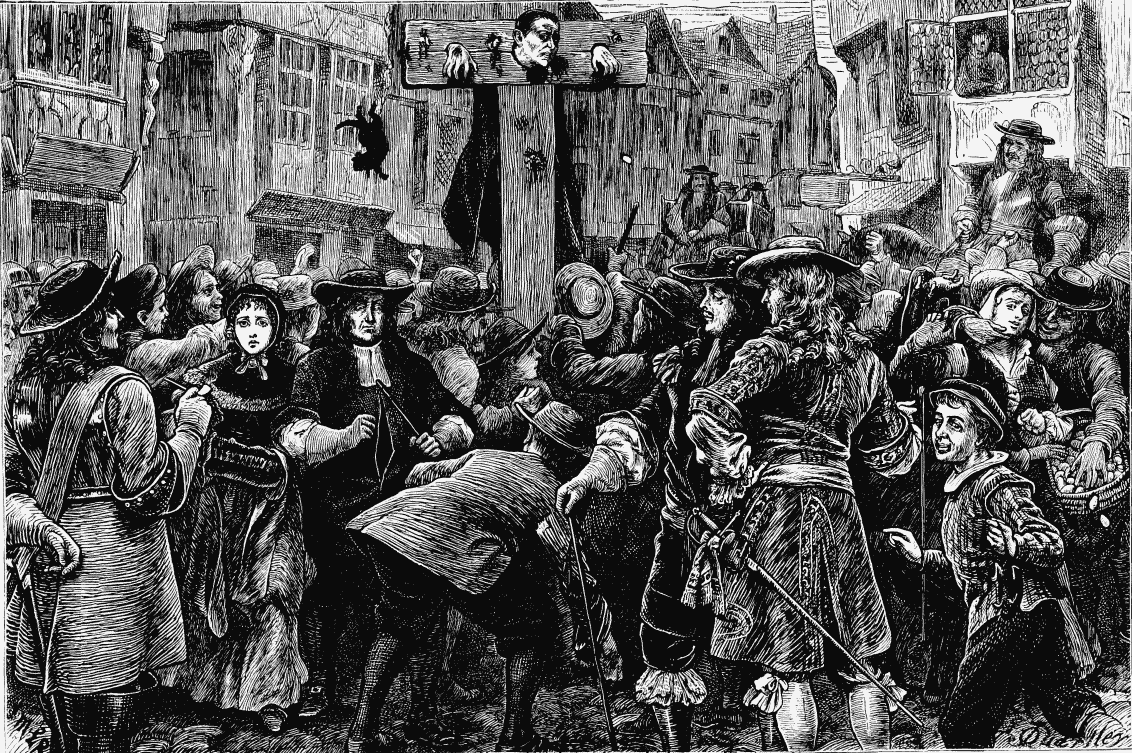
Titus Oates In the Pillory (see page 22).