Old and New London: Volume 1. Originally published by Cassell, Petter & Galpin, London, 1878.
This free content was digitised by double rekeying. Public Domain.
Walter Thornbury, 'The Temple: Church and precinct (part 1 of 3)', in Old and New London: Volume 1(London, 1878), British History Online https://prod.british-history.ac.uk/old-new-london/vol1/pp149-158 [accessed 9 May 2025].
Walter Thornbury, 'The Temple: Church and precinct (part 1 of 3)', in Old and New London: Volume 1(London, 1878), British History Online, accessed May 9, 2025, https://prod.british-history.ac.uk/old-new-london/vol1/pp149-158.
Walter Thornbury. "The Temple: Church and precinct (part 1 of 3)". Old and New London: Volume 1. (London, 1878), British History Online. Web. 9 May 2025. https://prod.british-history.ac.uk/old-new-london/vol1/pp149-158.
In this section
CHAPTER XIV.
THE TEMPLE CHURCH AND PRECINCT.
The Temple Church—Its Restorations—Discoveries of Antiquities—The Penitential Cell—Discipline in the Temple—The Tombs of the Templars in the "Round"—William and Gilbert Marshall—Stone Coffins in the Churchyard—Masters of the Temple—The "Judicious" Hooker—Edmund Gibbon, the Historian—The Organ in the Temple Church—The Rival Builders—"Straw Bail"—History of the Precinct—Chaucer and the Friar—His Mention of the Temple—The Serjeants—Erection of New Buildings—The "Roses"—Sumptuary Edicts—The Flying Horse.
The round church of the Temple is the finest of the four round churches still existing in England. The Templars did not, however, always build round towers, resembling the Temple at Jerusalem, though such was generally their practice. The restoration of this beautiful relic was one of the first symptoms of the modern Gothic revival.
In the reign of Charles II. the body of the church was filled with formal pews, which concealed the bases of the columns, while the walls were encumbered, to the height of eight feet from the ground, with oak wainscoting, which was carried entirely round the church, so as to hide the elegant marble piscina, the interesting almeries over the high altar, and the sacrarium on the eastern side of the edifice. The elegant Gothic arches connecting the round with the square church were choked up with an oak screen and glass windows and doors, and with an organ gallery adorned with Corinthian columns, pilasters, and Grecian ornaments, which divided the building into two parts, altogether altered its original character and appearance, and sadly marring its architectural beauty. The eastern end of the church was at the same time disfigured by an enormous altar-piece in the classic style, decorated with Corinthian columns and Grecian cornices and entablatures, and with enrichments of cherubims and wreaths of fruit, flowers, and leaves, heavy and cumbrous, and quite at variance with the Gothic character of the building. A large pulpit and carved sounding-board were erected in the middle of the dome, and the walls and whinns were encrusted and disfigured with hideous mural monuments and pagan trophies of forgotten wealth and vanity.
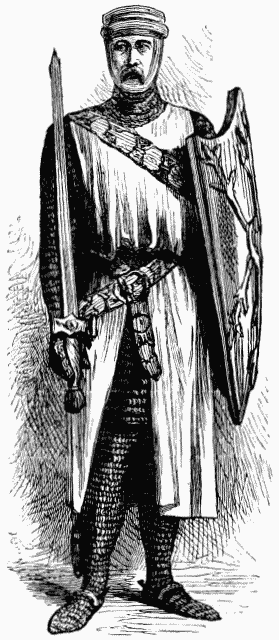
A KNIGHT TEMPLAR.
The following account of the earliest repairs of the Temple Church is given in "The New View of London": "Having narrowly escaped the flames in 1666, it was in 1682 beautified, and the curious wainscot screen set up. The south-west part was, in the year 1695, new built with stone. In the year 1706 the church was wholly new whitewashed, gilt, and painted within, and the pillars of the round tower wainscoted with a new battlement and buttresses on the south side, and other parts of the outside were well repaired. Also the figures of the Knights Templars were cleaned and painted, and the iron-work enclosing them new painted and gilt with gold. The east end of the church was repaired and beautified in 1707." In 1737 the exterior of the north side and east end were again repaired.
The first step towards the real restoration of the Temple Church was made in 1825. It had been generally repaired in 1811, but in 1825 Sir Robert Smirke restored the whole south side externally and the lower part of the circular portion of the round church. The stone seat was renewed, the arcade was restored, the heads which had been defaced or removed were supplied. The wainscoting of the columns was taken away, the monuments affixed to some of the columns were removed, and the position of others altered. There still remained, however, monuments in the round church materially affecting the relative proportions of the two circles; the clustered columns still retained their incrustations of paint, plaster, and whitewash; the three archway entrances into the oblong church remained in their former state, detaching the two portions from each other, and entirely destroying the perspective which those arches afforded.
When the genuine restoration was commenced in 1845, the removal of the beautifications and adornments which had so long disfigured the Temple Church, was regarded as an act of vandalism. Seats were substituted for pews, and a smaller pulpit and reading-desk supplied more appropriate to the character of the building. The pavement was lowered to its original level; and thus the bases of the columns became once more visible. The altar screen and railing were taken down. The organ was removed, and thus all the arches from the round church to the body of the oblong church were thrown open. By this alteration the character of the church was shown in its original beauty.
In the summer of 1840, the two Societies of the Inner and Middle Temple had the paint and whitewash scraped off the marble columns and ceiling. The removal of the modern oak wainscoting led to the discovery of a very beautiful double marble piscina near the east end of the south side of the building, together with an adjoining elegantly-shaped recess, and also a picturesque Gothic niche on the north side of the church.
On taking up the modern floor, remains of the original tesselated pavement were discovered. When the whitewash and plaster were removed from the ceiling it was found in a dangerous condition. There were also found were remains of ancient decorative paintings and rich ornaments worked in gold and silver; but they were too fragmentary to give an idea of the general pattern. Under these circumstances it was resolved to redecorate the ceiling in a style corresponding with the ancient decorative paintings observable in many Gothic churches in Italy and France.
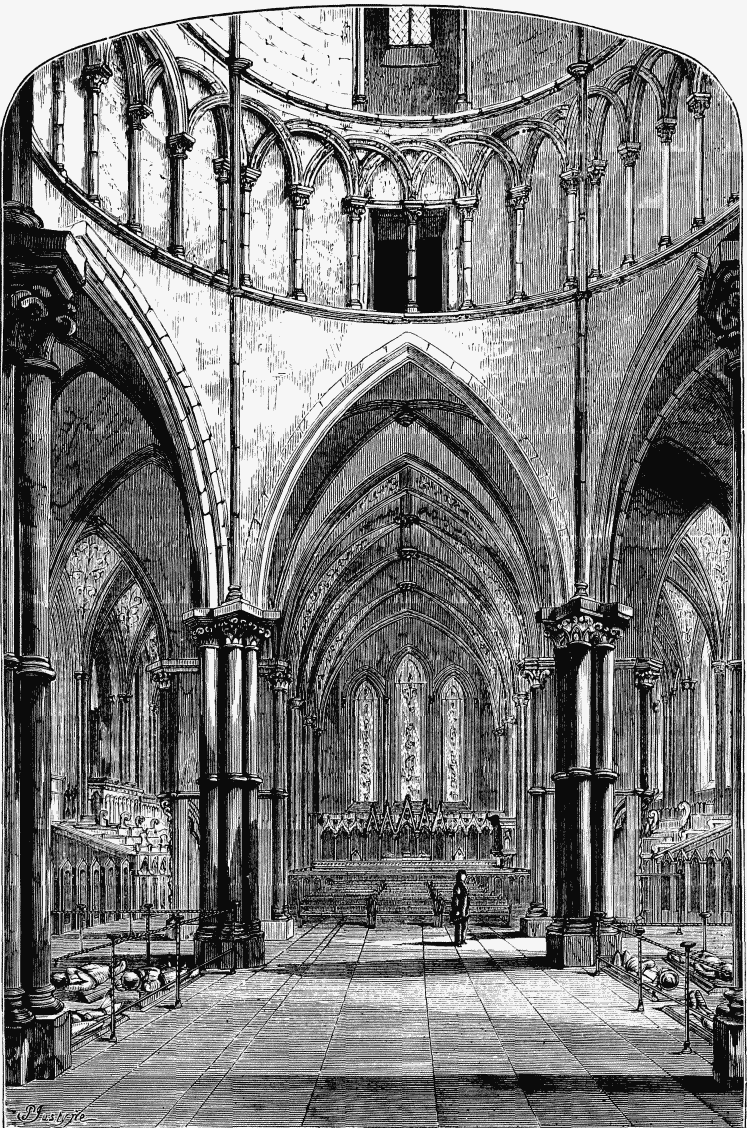
INTERIOR OF THE TEMPLE CHURCH (see page 150).
As the plaster and whitewash were removed it was found that the columns were of the most beautiful Purbeck marble. The six elegant clustered columns in the round tower had been concealed with a thick coating of Roman cement, which had altogether concealed the graceful form of the mouldings and carved foliage of their capitals. Barbarous slabs of Portland stone had been cased round their bases and entirely altered their character. All this modern patchwork was thrown away; but the venerable marble proved so mutilated that new columns were found necessary to support the fabric. These are exact imitations of the old ones. The six elegant clustered columns already alluded to, however, needed but slight repair. Almost all the other marble-work required renewal, and a special messenger was despatched to Purbeck to open the ancient quarries.
Above the western doorway was discovered a beautiful Norman window, composed of Caen stone. The porch before the western door of the Temple Church, which formerly communicated with an ancient cloister leading to the hall of the Knights Templars, had been filled up with rubbish to a height of nearly two feet above the level of the ancient pavement, so that all the bases of the magnificent Norman doorway were entirely hidden from view.
Previous to the recent restoration the round tower was surmounted by a wooden, flat, whitewashed ceiling, altogether different from the ancient roof. This ceiling and the timber roof above it have been entirely removed, and replaced by the present elegant and substantial roof, which is composed of oak, protected externally by sheet copper, and has been painted by Mr. Willement in accordance with an existing example of decorative painting in an ancient church in Sicily. Many buildings were also removed to give a clearer view of the fine old church.
"Among the many interesting objects," says Mr. Addison, "to be seen in the ancient church of the Knights Templars is a penitential cell, a dreary place of solitary confinement formed within the thick wall of the building, only four feet six inches long and two feet six inches wide, so narrow and small that a grown person cannot lie down within it. In this narrow prison the disobedient brethren of the ancient Templars were temporarily confined in chains and fetters, 'in order that their souls might be saved from the eternal prison of hell.' The hinges and catch of a door, firmly attached to the doorway of this dreary chamber, still remain, and at the bottom of the staircase is a stone recess or cupboard, where bread and water were placed for the prisoner. In this cell Brother Walter le Bacheler, Knight, and Grand Preceptor of Ireland, is said to have been starved to death for disobedience to his superior, the Master of the Temple. His body was removed at daybreak and buried by Brother John de Stoke and Brother Radulph de Barton in the middle of the court between the church and the hall."
The Temple discipline in the early times was very severe: disobedient brethren were scourged by the Master himself in the Temple Church, and frequently whipped publicly on Fridays in the church. Adam de Valaincourt, a deserter, was sentenced to eat meat with the dogs for a whole year, to fast four days in the week, and every Monday to present himself naked at the high altar to be publicly scourged by the officiating priest.
At the time of the restoration of the church stained glass windows were added, and the panels of the circular vaulting were emblazoned with the lamb and horse—the devices of the Inner and Middle Temple—and the Beauseant, or black and white banner of the Templars.
The mail-clad effigies on the pavement of the "Round" of the Temple Church are not monuments of Knights Templars, but of "Associates of the Temple," persons only partially admitted to the privileges of the powerful Order. During the last repairs there were found two Norman stone coffins and four ornamented leaden coffins in small vaults beneath these effigies, but not in their original positions. Stow, in 1598, speaks of eight images of armed knights in the round walk. The effigies have been restored by Mr. Richardson, the sculptor. The most interesting of these represents Geoffrey de Magnaville, Earl of Essex, a bold baron, who fought against King Stephen, sacked Cambridge, and plundered Ramsey Abbey. He was excommunicated, and while besieging Burwell Castle was struck by an arrow from a crossbow just as he had taken off his helmet to get air. The Templars, not daring to bury him, soldered him up in lead, and hung him on a crooked tree in their riverside orchard. The corpse being at last absolved, the Templars buried it before the west door of their church. He is to be known by a long, pointed shield charged with rays on a diamonded field. The next figure, of Purbeck marble in low relief, is supposed to be the most ancient of all. The shield is kite-shaped, the armour composed of rude rings—name unknown. Vestiges of gilding were discovered upon this monument. The two effigies on the north-east of the "Round" are also anonymous. They are the tallest of all the stone brethren: one of them is straight-legged; the crossed legs of his comrade denote a Crusading vow. The feet of the first rests on two grotesque human heads, probably Infidels; the second wears a mouth guard like a respirator. Between the two figures is the copestone lid of an ancient sarcophagus, probably that of a Master or VisitorGeneral of the Templars, as it has the head of the cross which decorates it adorned with a lion's head, and the foot rests on the head of a lamb, the joint emblems of the Order of the Templars. During the excavations in the "Round," a magnificent Purbeck marble sarcophagus, the lid decorated with a foliated cross, was dug up and re-interred.
On the south side of the "Round," between two columns, his feet resting upon a lion, reposes a great historical personage, William Marshall, the Protector of England during the minority of King Henry III., a warrior and a statesman whose name is sullied by no crimes. The features are handsome, and the whole body is wrapped in chain mail. A Crusader in early life, the earl became one of Richard Cæur de Lion's vicegerents during his absence in Palestine. He fought in Normandy for King John, helped in the capture of Prince Arthur and his sister, urged the usurper to sign Magna Charta, and secured the throne for Prince Henry. Finally, he defeated the French invaders, routed the French at sea, and died, in the fulness of years, a warrior whose deeds had been notable, a statesman whose motives could seldom be impugned. Shakespeare, with ever a keen eye for great men, makes the earl the interceder for Prince Arthur. He was a great benefactor of the brethren of the Chivalry of the Temple.
By the side of the earl reposes his warlike son William Marshall the younger, cut in freestone. He was one of the chief leaders of the Barons against John, and in Henry's reign he overthrew Prince Llewellyn, and slew 8,000 wild Welsh. He fought with credit in Brittany and Ireland, and eventually married Eleanor, the king's sister. He gave an estate to the Templars. The effigy is clad in a shirt of ring mail, above which is a loose garment, girded at the waist. The shield on the left arm bears a lion rampant.
Near the western doorway reclines the mailed effigy of Gilbert Marshall, Earl of Pembroke, third son of the Protector. He is in the act of drawing a sword, and his left foot rests on a winged dragon. This earl, at the murder of a brother in Ireland, succeeded to the title, and married Margaret, a daughter of the King of Scotland. He was just starting for the Crusades, when he was killed by a fall from his horse, in a tournament held at Ware, (1241). Like the other Marshalls, he was a benefactor of the Temple, and, like all the four sons of the Protector, died without issue, in the reign of Henry III., the family becoming extinct with him. Matthew Paris declared that the race had been cursed by the Bishop of Fernes, from whom the Protector had stolen lands. The bishop, says the chronicler, with great awe came with King Henry to the Temple Church, and, standing at the earl's tomb, promised the dead man absolution if the lands were returned. No restitution was made, so the curse fell on the doomed race. All these Pembrokes wear chain hoods and have animals recumbent at their feet.
The name of a beautiful recumbent mailed figure next Gilbert Marshall is unknown, and near him, on the south side of the "Round," rests the everpraying effigy of Robert, Lord de Ros. This lord was no Templar, for he has no beard, and wears flowing hair, contrary to the rules of the Order. His shield bears three water buckets. The figure is cut out of yellow Roach Abbey stone. The armour is linked. This knight was fined £800 by Richard Cœur de Lion for allowing a French prisoner of consequence to escape from his custody. He married a daughter of a King of Scotland, was Sheriff of Cumberland, helped to extort Magna Charta from King John, and gave much public property to the Templars.
During the repairs of the round tower several sarcophagi of Purbeck marble were discovered. On the coffins being removed while the tower was being propped, the bodies all crumbled to dust. The sarcophagi were all reinterred in the centre of the "Round."
During the repairs of 1850 the workmen discovered and stole an ancient seal of the Order; it had the name of Berengarius, and on one side was represented the Holy Sepulchre. "The churchyard abounds," Mr. Addison says, "with ancient stone coffins. According to Burton, an antiquary of Elizabeth's time, there then existed in the Temple Church a monument to a Visitor-General of the Order. Among other distinguished persons buried in the Temple Church, for so many ages a place of special sanctity, was William Plantagenet, fifth son of Henry III., who died when a youth. Henry III. himself, had at one time resolved to be buried "with the brethren of the Chivalry of the Temple, expecting and hoping that, through our Lord and Saviour, it will greatly contribute to the salvation of our soul." Queen Eleanor also provided for her interment in the Temple, but it was otherwise decreed.
In the triforium of the Temple Church have been packed away, like lumber, the greater part of the clumsy monuments that once disfigured the walls and columns below. In this strange museum lord chancellors, councillors of state, learned benchers, barons of the exchequer, masters of the rolls, treasurers, readers, prothonotaries, poets, and authors jostle each other in dusty confusion. At the entrance, under a canopy, is the recumbent figure of the great lawyer of Elizabeth's time, Edmund Plowden. This grave and wise man, being a staunch Romanist, was slighted by the Protestant Queen. It is said that he was so studious in his youth that at one period he never went out of the Temple precincts for three whole years. He was Treasurer of the Middle Temple the year the hall was built.
Selden (that great writer on international law, whose "Mare clausum" was a reply to the "Mare liberum" of Grotius) is buried to the left of the altar, the spot being marked by a monument of white marble. "His grave," says Aubrey, "was about ten feet deepe or better, walled up a good way with bricks, of which also the bottome was paved, but the sides at the bottome for about two foot high were of black polished marble, wherein his coffin (covered with black bayes) lyeth, and upon that wall of marble was presently lett downe a huge black marble stone of great thicknesse, with this inscription—'Hic jacet corpus Johannis Seldeni, qui obijt 30 die Novembris, 1654.' Over this was turned an arch of brick (for the house would not lose their ground), and upon that was throwne the earth," &c.
There is a monument in the triforium to Edmund Gibbon, a herald and an ancestor of the historian. The great writer alluding to this monment says—"My family arms are the same which were borne by the Gibbons of Kent, in an age when the College of Heralds religiously guarded the distinctions of blood and name—a lion rampant gardant between three schollop shells argent, on a field azure. I should not, however, have been tempted to blazon my coat of arms were it not connected with a whimsical anecdote. About the reign of James I., the three harmless schollop shells were changed by Edmund Gibbon, Esq., into three ogresses, or female cannibals, with a design of stigmatising three ladies, his kinswomen, who had provoked him by an unjust lawsuit. But this singular mode of revenge, for which he obtained the sanction of Sir William Seager, King-at-Arms, soon expired with its author; and on his own monument in the Temple Church the monsters vanish, and the three schollop shells resume their proper and hereditary place."
At the latter end of Charles II.'s reign the organ in the Temple Church became the subject of a singular contest, which was decided by a most remarkable judge. The benchers had determined to have the best organ in London; the competitors for the building were Smith and Harris. Father Smith, a German, was renowned for his care in choosing wood without knot or flaw, and for throwing aside every metal or wooden pipe that was not perfect and sound. His stops were also allowed by all to be singularly equal and sweet in tone. The two competitors were each to erect an organ in the Temple Church, and the best one was to be retained. The competition was carried on with such violence that some of the partisans almost ruined themselves by the money they expended. The night preceding the trial the too zealous friends of Harris cut the bellows of Smith's organ, and rendered it for the time useless. Drs. Blow and Purcell were employed to show the powers of Smith's instrument, and the French organist of Queen Catherine performed on Harris's. The contest continued, with varying success, for nearly a twelvemonth. At length Harris challenged his redoubtable rival to make certain additional reed stops, vox humana, cremona, double bassoon and other stops, within a given time. The controversy was at last terminated by Lord Chief Justice Jefferies—the cruel and debauched Jefferies, who was himself an accomplished musician—deciding in favour of Father Smith. Part of Harris's rejected organ was erected at St. Andrew's, Holborn, part at Christ Church Cathedral, Dublin. Father Smith, in consequence of his success at the Temple, was employed to build an organ for St. Paul's, but Sir Christopher Wren would never allow the case to be made large enough to receive all the stops. "The sound and general mechanism of modern instruments," says Mr. Burge, "are certainly superior to those of Father Smith's, but for sweetness of tone I have never met in any part of Europe with pipes that have equalled his."
In the reign of James I. there was a great dispute between the Custos of the Temple and the two Societies. This sinecure office, the gift of the Crown, was a rectory without tithes, and the Custos was dependent upon voluntary contributions. The benchers, irritated at Dr. Micklethwaite's arrogant pretensions, shut the doctor out from their dinners. In the reign of Charles I., the doctor complained to the king that he received no tithes, was refused precedence as Master of the Temple, was allowed no share in the deliberations, was not paid for his supernumerary sermons, and was denied ecclesiastical jurisdiction. The doctor thereupon locked up the church and took away the keys; but Noy, the Attorney-General, snubbed him, and called him "elatus et superbus;" and he got nothing, after all, but hard words, for his petition.
The learned and judicious Hooker, author of "The Ecclesiastical Polity," was for six years Master of the Temple—"a place," says Izaak Walton, "which he accepted rather than desired." Travers, a disciple of Cartwright the Noncomforn ist, was the lecturer; so Hooker, it was said, preached Canterbury in the forenoon, and Travers Geneva in the afternoon. The benchers were divided, and Travers being at last silenced by the archbishop, Hooker resigned, and in his quiet parsonage of Boscombe renewed the contest in print, in his "Ecclesiastical Polity."
When Bishop Sherlock, was Master of the Temple,
the sees of Canterbury and London were vacant
about the same time (1748); this occasioned an
epigram upon Sherlock,—
"At the Temple one day, Sherlock taking a boat,
The waterman asked him, 'Which way will you float?'
'Which way?' says the Doctor; 'why, fool, with the stream!'
To St. Paul's or to Lambeth was all one to him."
The tide in favour of Sherlock was running to St. Paul's. He was made Bishop of London.
During the repairs of 1827 the ancient freestone chapel of St. Anne, which stood on the south side of the "Round," was ruthlessly removed. We had less reverence for antiquity then. The upper storey communicated with the Temple Church by a staircase opening on the west end of the south aisle of the choir; the lower joined the "Round" by a doorway under one of the arches of the circular arcade. The chapel anciently opened upon the cloisters, and formed a private way from the convent to the church. Here the Papal legate and the highest bishops frequently held conferences; and on Sunday mornings the Master of the Temple held chapters, enjoined penances, made up quarrels, and pronounced absolution. The chapel of St. Anne was in the old time much resorted to by barren women, who there prayed for children.
In Charles II.'s time, according to "Hudibras,"
"straw bail" and low rascals of that sort lingered
about the Round, waiting for hire. Butler says:—
"Retain all sorts of witnesses
That ply i' the Temple, under trees,
Or walk the Round with Knights o' th' Posts,
About the cross-legg'd knights, their hosts;
Or wait for customers between
The pillar rows in Lincoln's Inn."
In James I.'s time the Round, as we find in Ben Jonson, was a place for appointments; and in 1681 Otway describes bullies of Alsatia, with flapping hats pinned up on one side, sandy, weather-beaten periwigs, and clumsy iron swords clattering at their heels, as conspicuous personages among the Knights of the Posts and the other peripatetic philosophers of the Temple walks.
We must now turn to the history of the whole precinct. When the proud Order was abolished by the Pope, Edward II. granted the Temple to Aymer de Valence, Earl of Pembroke, who, however, soon surrendered it to the king's cousin, the Earl of Lancaster, who let it, at their special request, to the students and professors of the common laws; the colony then gradually becoming an organised and collegiate body, Edward I. having authorised laymen for the first time to read and plead causes.
Hugh le Despenser for a time held the Temple, and on his execution Edward III. appointed the Mayor of London its guardian. The mayor closing the watergate caused much vexation to the lawyers rowing by boat to Westminster, and the king had to interfere. In 1333 the king farmed out the Temple rents at £25 a year. In the meantime, the Knights Hospitallers, affecting to be offended at the desecration of holy ground—the Bishop of Ely's lodgings, a chapel dedicated to à Becket, and the door to the Temple Hall—claimed the forfeited spot. The king granted their request, the annual revenue of the Temple then being £73 6s. 11d., equal to about £1,000 of our present money. In 1340, in consideration of £100 towards an expedition to France, the warlike king made over the residue of the Temple to the Hospitallers, who instantly endowed the church with lands and one thousand fagots a year from Lillerton Wood to keep up the church fires.
In this reign Chaucer, who is supposed to have been a student of the Middle Temple, and who is said to have once beaten an insolent Franciscan friar in Fleet Street, gives a eulogistic sketch of a Temple manciple, or purveyor of provisions, in the prologue to his wonderful "Canterbury Tales."
"A gentil manciple was there of the Temple
Of whom achatours mighten take ensample,
For to ben wise in bying of vitàille;
For, whether that he paid or toke by taille,
Algate he waited so in his achate
That he was aye before in good estate.
Now is not that of God a full fayre grace
That swiche a lewèd mannès wit shall face
The wisdom of an hepe of lerned men ?
"Of maisters had he more than thries ten,
That were of law expert and curious;
Of which there was a dosein in that hous
Worthy to ben stewardes of rent and land
Of any lord that is in Engleland:
To maken him live by his propre good,
In honour detteles; but if he were wood,
Or live as scarsly as him list desire,
And able for to helpen all a shire,
In any cos that mighte fallen or happe:
And yet this manciple sett 'hir aller cappe."
In the Middle Temple Chaucer is supposed to have formed the acquaintanceship of his graver contemporary, "the moral Gower."
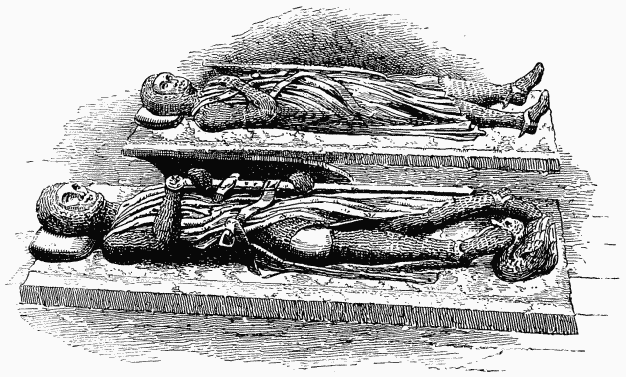
TOMBS OF KNIGHTS TEMPLARS (see page 152).
Many of the old retainers of the Templars became servants of the new lawyers, who had ousted their masters. The attendants at table were still called paniers, as they had formerly been. The dining in pairs, the expulsion from hall for misconduct, and the locking out of chambers were old customs also kept up. The judges of Common Pleas retained the title of knight, and the Fratres Servientes of the Templars arose again in the character of learned serjeants-at-law, the coif of the modern serjeant being the linen coif of the old Freres Serjens of the Temple. The coif was never, as some suppose, intended to hide the tonsure of priests practising law contrary to ecclesiastical prohibition. The old ceremony of creating serjeantsat-law exactly resembles that once used for receiving Fratres Servientes into the fraternity of the Temple.
In Wat Tyler's rebellion the wild men of Kent poured down on the dens of the Temple lawyers, pulled down their houses, carried off the books, deeds, and rolls of remembrance, and burnt them in Fleet Street, to spite the Knights Hospitallers. Walsingham, the chronicler, indeed, says that the rebels—who, by the by, claimed only their rights—had resolved to decapitate all the lawyers of London, to put an end to all the laws that had oppressed them, and to clear the ground for better times. In the reign of Henry VI. the overgrown society of the Temple divided into two halls, or rather the original two halls of the knights and Fratres Servientes separated into two societies. Brooke, the Elizabethan antiquary, says: "To this day, in memory of the old custom, the benchers or ancients of the one society dine once every year in the hall of the other society."
Sir John Fortescue, Chief Justice of the King's Bench in the reign of Henry VI., computed the annual expenses of each law student at more than £28—("£450 of our present money"—Addison). The students were all gentlemen by birth, and at each Inn of Court there was an academy, where singing, music, and dancing were taught. On festival days, after the offices of the Church, the students employed themselves in the study of history and in reading the Scriptures. Any student expelled one society was refused admission to any of the other societies. A manuscript (temp. Henry VIII.) in the Cotton Library dwells much on the readings, mootings, boltings, and other practices of the Temple students, and analyses the various classes of benchers, readers, cupboardmen, inner barristers, outer barristers, and students. The writer also mentions the fact that in term times the students met to talk law and confer on business in the church, which was, he says, as noisy as St. Paul's. When the plague broke out the students went home to the country.
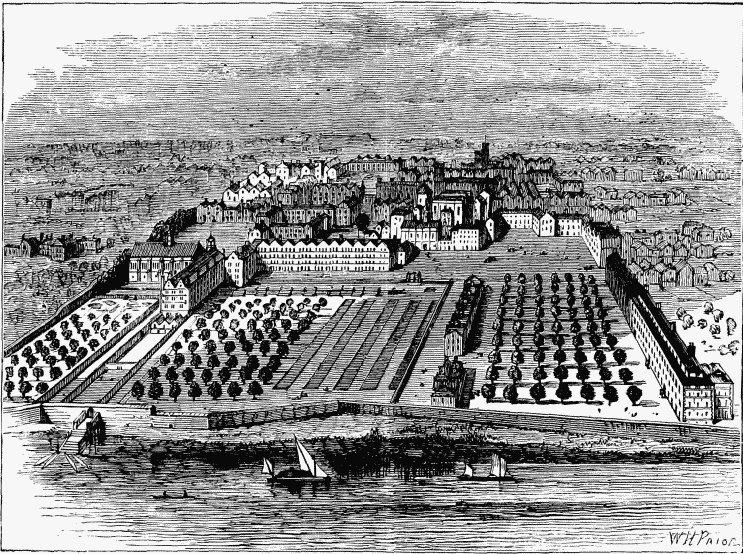
THE TEMPLE IN 1671. (FROM AN OLD BIRD'S-EYE VIEW IN THE INNER TEMPLE.)
The Society of the Inner Temple was very active (says Mr. Foss) during the reign of Henry VIII. in the erection of new buildings. Several houses for chambers were constructed near the library, and were called Pakington's Rents, from the name of the treasurer who superintended them. Henry Bradshaw, treasurer in the twenty-sixth year, gave his name to another set then built, which it kept until Chief Baron Tanfield resided there in the reign of James I., since which it has been called Tanfield Court. Other improvements were made about the same period, one of these being the construction of a new ceiling to the hall and the erection of a wall between the garden and the Thames.
The attention paid by the governors of the house both to the morals and dress of its members is evidenced by the imposition, in the thirteenth year of the reign of Henry VIII., of a fine of 6s. 8d. on any one who should exercise the plays of "shove-grote" or "slyp-grote," and by the mandate afterwards issued in the thirty-eighth year of the same reign, that students should reform themselves in their cut, or disguised apparel, and should not have long beards.
It is in the Temple Gardens that Shakespeare—relying, probably, on some old tradition which
does not exist in print—has laid one of the scenes
of his King Henry VI.—that, namely, in which the
partisans of the rival houses of York and Lancaster first assume their distinctive badges of the
white and red roses:—
"Suffolk. Within the Temple Hall we were too loud;
The garden here is more convenient.
* * * *
"Plantagenet. Let him that is a true-born gentleman,
And stands upon the honour of his birth,
If he suppose that I have pleaded truth,
From off this brier pluck a white rose with me.
"Somerset. Let him that is no coward, nor no flatterer,
But dare maintain the party of the truth,
Pluck a red rose from off this thorn with me.
* * * *
"Plantagenet. Hath not thy rose a canker, Somerset?
"Somerset. Hath not thy rose a thorn, Plantagenet?
* * * *
"Warwick. This brawl to-day,
Grown to this faction in the Temple Garden,
Shall send, between the red rose and the white,
A thousand souls to death and deadly night."
King Henry VI., Part I., Act ii., sc. 4.
The books of the Middle Temple do not commence till the reign of King Henry VII., the first treasurer named in them being John Brooke, in the sixteenth year of Henry VII. (1500-1). Readers were not appointed till the following year, the earliest being John Vavasour—probably son of the judge, and not, as Dugdale calls him, the judge himself, who had then been on the bench for twelve years. Members of the house might be excused from living in commons on account of their wives being in town, or for other special reasons (Foss).
In the last year of Philip and Mary (1558) eight gentlemen of the Temple were expelled the society and committed to the Fleet for wilful disobedience to the Bench, but on their humble submission they were readmitted. A year before this a severe Act of Parliament was passed, prohibiting Templars wearing beards of more than three weeks' growth, upon pain of a forty-shilling fine, and double for every week after monition. The young lawyers were evidently getting too foppish. They were required to cease wearing Spanish cloaks, swords, bucklers, rapiers, gowns, hats, or daggers at their girdles. Only knights and benchers were to display doublets or hose of any light colour, except scarlet and crimson, or to affect velvet caps, scarf-wings to their gowns, white jerkins, buskins, velvet shoes, double shirtcuffs, or feathers or ribbons in their caps. Moreover, no attorney was to be admitted into either house. These monastic rules were intended to preserve the gravity of the profession, and must have pleased the Poloniuses and galled the Mer.cutios of those troublous days.
In Elizabeth's days Master Gerard Leigh, a pedantic scholar of the College of Heralds, persuaded the misguided Inner Temple to abandon the old Templar arms—a plain red cross on a shield argent, with a lamb bearing the banner of the sinless profession, surmounted by a red cross. The heraldic euphuist substituted for this a flying Pegasus striking out the fountain of Hippocrene with its hoofs, with the appended motto of "Volat ad astera virtus," a recondite allusion to men, like Chaucer and Gower, who, it is said, had turned from lawyers to poets.