Old and New London: Volume 1. Originally published by Cassell, Petter & Galpin, London, 1878.
This free content was digitised by double rekeying. Public Domain.
Walter Thornbury, 'Fleet Street: Tributaries (continued)', in Old and New London: Volume 1(London, 1878), British History Online https://prod.british-history.ac.uk/old-new-london/vol1/pp112-123 [accessed 19 April 2025].
Walter Thornbury, 'Fleet Street: Tributaries (continued)', in Old and New London: Volume 1(London, 1878), British History Online, accessed April 19, 2025, https://prod.british-history.ac.uk/old-new-london/vol1/pp112-123.
Walter Thornbury. "Fleet Street: Tributaries (continued)". Old and New London: Volume 1. (London, 1878), British History Online. Web. 19 April 2025. https://prod.british-history.ac.uk/old-new-london/vol1/pp112-123.
In this section
CHAPTER X.
FLEET STREET TRIBUTARIES.
Dr. Johnson in Bolt Court—His motley Household—His Life there—Still existing—The gallant "Lumber Troop"—Reform Bill Riots—Sir Claudius Hunter—Cobbett in Bolt Court—The Bird Boy—The Private Soldier—In the House—Dr. Johnson in Gough Square—Busy at the Dictionary—Goldsmith in Wine Office Court—Selling "The Vicar of Wakefield"—Goldsmith's Troubles—Wine Office Court—The Old "Cheshire Cheese."
Of all the nooks of London associated with the memory of that good giant of literature, Dr. Johnson, not one is more sacred to those who love that great and wise man than Bolt Court. To this monastic court Johnson came in 1776, and remained till that December day in 1784, when a procession of all the learned and worthy men who honoured him followed his body to its grave in the Abbey, near the feet of Shakespeare and by the side of Garrick. The great scholar, whose ways and sayings, whose rough hide and tender heart, are so familiar to us—thanks to that faithful parasite who secured an immortality by getting up behind his triumphal chariot—came to Bolt Court from Johnson's Court, whither he had flitted from Inner Temple Lane, where he was living when the young Scotch barrister who was afterwards his biographer first knew him. His strange household of fretful and disappointed almspeople seems as well known as our own. At the head of these pensioners was the daughter of a Welsh doctor, (a blind old lady named Williams), who had written some trivial poems; Mrs. Desmoulins, an old Staffordshire lady, her daughter, and a Miss Carmichael. The relationships of these fretful and quarrelsome old maids Dr. Johnson has himself sketched, in a letter to Mr. and Mrs. Thrale:—"Williams hates everybody; Levett hates Desmoulins, and does not love Williams; Desmoulins hates them both; Poll (Miss Carmichael) loves none of them." This Levett was a poor eccentric apothecary, whom Johnson supported, and who seems to have been a charitable man.
The annoyance of such a menagerie of angular oddities must have driven Johnson more than ever to his clubs, where he could wrestle with the best intellects of the day, and generally retire victorious. He had done nearly all his best work by this time, and was sinking into the sere and yellow leaf, not, like Macbeth, with the loss of honour, but with love, obedience, troops of friends, and golden opinions from all sorts of people. His Titanic labour, the Dictionary, he had achieved chiefly in Gough Square; his "Rasselas"—that grave and wise Oriental story—he had written in a few days, in Staple's Inn, to defray the expenses of his mother's funeral. In Bolt Court he, however, produced his "Lives of the Poets," a noble compendium of criticism, defaced only by the bitter Tory depreciation of Milton, and injured by the insertion of many worthless and the omission of several good poets.
It is pleasant to think of some of the events that happened while Johnson lived in Bolt Court. Here he exerted himself with all the ardour of his nature to soothe the last moments of that wretched man, Dr. Dodd, who was hanged for forgery. From Bolt Court he made those frequent excursions to the Thrales, at Streatham, where the rich brewer and his brilliant wife gloried in the great London lion they had captured. To Bolt Court came Johnson's friends Reynolds and Gibbon, and Garrick, and Percy, and Langton; but poor Goldsmith had died before Johnson left Johnson's Court. To Bolt Court he stalked home the night of his memorable quarrel with Dr. Percy, no doubt regretting the violence and boisterous rudeness with which he had attacked an amiable and gifted man. From Bolt Court he walked to service at St. Clement's Church on the day he rejoiced in comparing the animation of Fleet Street with the desolation of the Hebrides. It was from Bolt Court Boswell drove Johnson to dine with General Paoli, a drive memorable for the fact that on that occasion Johnson uttered his first and only recorded pun.
Johnson was at Bolt Court when the Gordon Riots
broke out, and he describes them to Mrs. Thrale.
Boswell gives a pleasant sketch of a party at Bolt
Court, when Mrs. Hall (a sister of Wesley) was
there, and Mr. Allen, a printer; Johnson produced his silver salvers, and it was "a great
day." It was on this occasion that the conversation fell on apparitions, and Johnson, always
superstitious to the last degree, told the story of
hearing his mother's voice call him one day at
Oxford (probably at a time when his brain was overworked). On this great occasion also, Johnson,
talked at by Mrs. Hall and Mrs. Williams at the
same moment, gaily quoted the line from the
Beggars' Opera,—
"But two at a time there's no mortal can bear,"
and Boswell playfully compared the great man
to Captain Macheath. Imagine Mrs. Williams, old
and peevish; Mrs. Hall, lean, lank, and preachy;
Johnson, rolling in his chair like Polyphemus at a
debate; Boswell, stooping forward on the perpetual listen; Mr. Levett, sour and silent; Frank,
the black servant, proud of the silver salvers—and
you have the group as in a picture.
In Bolt Court we find Johnson now returning from pleasant dinners with Wilkes and Garrick, Malone and Dr. Burney; now sitting alone over his Greek Testament, or praying with his black servant, Frank. We like to picture him on that Good Friday morning (1783), when he and Boswell, returning from service at St. Clement's, rested on the stone seat at the garden-door in Bolt Court, talking about gardens and country hospitality.
Then, finally, we come to almost the last scene
of all, when the sick man addressed to his kind
physician, Brocklesby, that pathetic passage of
Shakespeare's,—
"Canst thou not minister to a mind diseased;
Pluck from the memory a rooted sorrow;
Raze out the written troubles of the brain;
And with some sweet oblivious antidote
Cleanse the stuffed bosom of that perilous stuff
Which weighs upon the heart ?"
Round Johnson's dying bed gathered many wise
and good men. To Burke he said, "I must be
in a wretched state indeed, when your company
would not be a delight to me." To another friend
he remarked solemnly, but in his old grand manner,
"Sir, you cannot conceive with what acceleration
I advance towards death." Nor did his old vehemence and humour by any means forsake him, for
he described a man who sat up to watch him
"as an idiot, sir; awkward as a turnspit when first
put into the wheel, and sleepy as a dormouse."
His remaining hours were spent in fervent prayer.
The last words he uttered were those of benediction upon the daughter of a friend who came to
ask his blessing.
Some years before Dr. Johnson's death, when the poet Rogers was a young clerk of literary proclivities at his father's bank, he one day stole surreptitiously to Bolt Court, to daringly show some of his fledgeling poems to the great Polyphemus of literature. He and young Maltby, an ancestor of the late Bishop of Durham, crept blushingly through the quiet court, and on arriving at the sacred door on the west side, ascended the steps and knocked at the door; but the awful echo of that knocker struck terror to the young debutants' hearts, and before Frank Barber, the Doctor's old negro footman, could appear, the two lads, like street-boys who had perpetrated a mischievous runaway knock, took to their heels and darted back into noisy Fleet Street. Mr. Jesse, who has collected so many excellent anecdotes, some even original, in his three large volumes on "London's Celebrated Characters and Places," says that the elder Mr. Disraeli, singularly enough, used in society to relate an almost similar adventure as a youth. Eager for literary glory, but urged towards the counter by his sober-minded relations, he enclosed some of his best verses to the celebrated Dr. Johnson, and modestly solicited from the terrible critic an opinion of their value. Having waited some time in vain for a reply, the ambitious Jewish youth at last (December 13, 1784) resolved to face the lion in his den, and rapping tremblingly (as his predecessor, Rogers), heard with dismay the knocker echo on the metal. We may imagine the feelings of the young votary at the shrine of learning, when the servant (probably Frank Barber), who slowly opened the door, informed him that Dr. Johnson had breathed his last only a few short hours before.
Mr. Timbs reminds us of another story of Dr. Johnson, which will not be out of place here. It is an excellent illustration of the keen sagacity and forethought of that great man's mind. One evening Dr. Johnson, looking from his dim Bolt Court window, saw the slovenly lamp-lighter of those days ascending a ladder (just as Hogarth has drawn him in the "Rake's Progress"), and fill the little receptacle in the globular lamp with detestable whale-oil. Just as he got down the ladder the dull light wavered out. Skipping up the ladder again, the son of Prometheus lifted the cover, thrust the torch he carried into the heated vapour rising from the wick, and instantly the ready flame sprang restored to life. "Ah," said the old seer, "one of these days the streets of London will be lighted by smoke."
Johnson's house (No. 8), according to Mr. Noble, was not destroyed by fire in 1819, as Mr. Timbs and other writers assert. The house destroyed was Bensley the printer's (next door to No. 8), the successor of Johnson's friend, Allen, who in 1772 published Manning's Saxon, Gothic, and Latin Dictionary, and died in 1780. In Bensley's destructive fire all the plates and stock of Dallaway's "History of Sussex" were consumed. Johnson's house, says Mr. Noble, was in 1858 purchased by the Stationers' Company, and fitted up as a cheap school (six shillings a quarter). In 1861 Mr. Foss, Master of the Company, initiated a fund, and since then a university scholarship has been founded—sic itur ad astra. The back room, first floor, in which the great man died, had been pulled down by Mr. Bensley, to make way for a staircase. Bensley was one of the first introducers of the German invention of steam-printing.
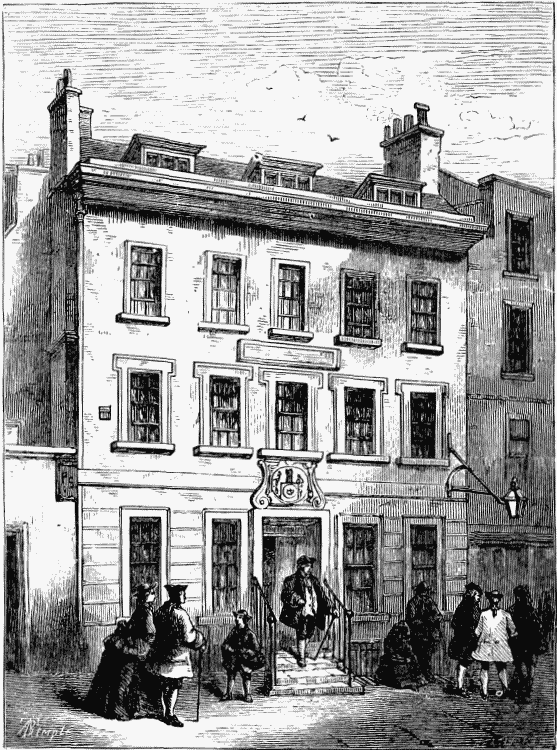
DR. JOHNSON'S HOUSE IN BOLT COURT (see page 112).
At "Dr. Johnson's" tavern, established forty years ago (now the Albert Club), the well-known society of the "Lumber Troop" once drained their porter and held their solemn smokings. This gallant force of supposititious fighting men "came out" with great force during the Reform Riots of 1830. These useless disturbances originated in a fussy, foolish warning letter, written by John Key, the Lord Mayor elect (he was generally known in the City as Don Key after this), to the Duke of Wellington, then as terribly unpopular with the English Reformers as he had been with the French after the battle of Waterloo, urging him (the duke) if he came with King William and Queen Adelaide to dine with the new Lord Mayor, (his worshipful self), to come "strongly and sufficiently guarded." This imprudent step greatly offended the people, who were also just then much vexed with the severities of Peel's obnoxious new police. The result was that the new king and queen (for the not overbeloved George IV. had only died in June of that year) thought it better to decline coming to the City festivities altogether. Great, then, was even the Tory indignation, and the fattest alderman trotted about, eager to discuss the grievance, the waste of half-cooked turtle, and the general folly and enormity of the Lord Mayor elect's conduct. Sir Claudius Hunter, who had shared in the Lord Mayor's fears, generously marched to his aid. In a published statement that he made, he enumerated the force available for the defence of the (in his mind) endangered City in the following way:—
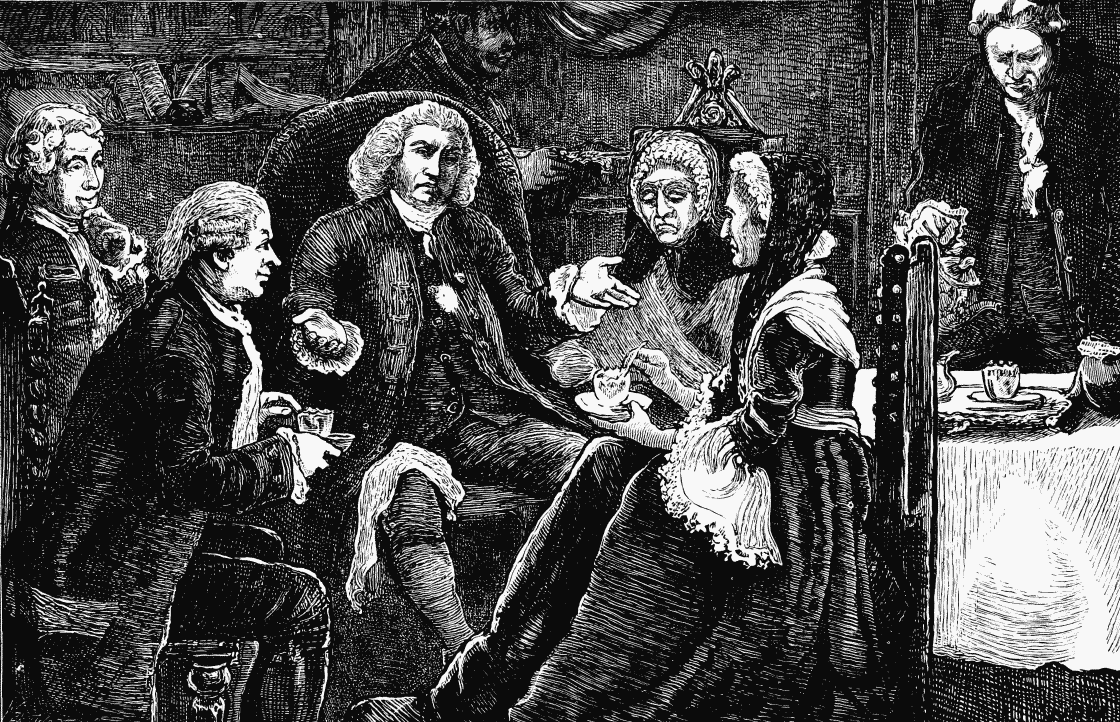
A TEA PARTY AT DR. JOHNSON'S (see page 113).
In the same statement Sir Claudius says:—"The Lumber Troop are a respectable smoking club, well known to every candidate for a seat in Parliament for London, and most famed for the quantity of tobacco they consume and the porter they drink, which, I believe (from my own observation, made nineteen years ago, when I was a candidate for that office), is the only liquor allowed. They were to have had no pay, and I am sure they would have done their best."
Along the line of procession, to oppose this civic force, the right worshipful but foolish man reckoned there would be some 150,000 persons. With all these aldermanic fears, and all these irritating precautions, a riot naturally took place. On Monday, November 8th, that glib, unsatisfactory man, Orator Hunt, the great demagogue of the day, addressed a Reform meeting at the Rotunda, in Blackfriars Road. At half-past eleven, when the Radical gentleman, famous for his white hat (the lode-star of faction), retired, a man suddenly waved a tricolour flag (it was the year, remember, of the Revolution in Paris), with the word "Reform" painted upon it, and a preconcerted cry was raised by the more violent of, "Now for the West End!" About one thousand men then rushed over Blackfriars bridge, shouting, "Reform!" "Down with the police!" "No Peel!" "No Wellington!" Hurrying along the Strand, the mob first proceeded to Earl Bathurst's, in Downing Street. A foolish gentleman of the house, hearing the cries, came out on the balcony, armed with a brace of pistols, and declared he would fire on the first man who attempted to enter the place. Another gentleman at this moment came out, and very sensibly took the pistols from his friend, on which the mob retired. The rioters were then making for the House of Commons, but were stopped by a strong line of police, just arrived in time from Scotland Yard. One hundred and forty more men soon joined the constables, and a general fight ensued, in which many heads were quickly broken, and the Reform flag was captured. Three of the rioters were arrested, and taken to the watch-house in the Almonry in Westminster. A troop of Royal Horse Guards (blue) remained during the night ready in the court of the Horse Guards, and bands of policemen paraded the streets.
On Tuesday the riots continued. About halfpast five p.m., 300 or 400 persons, chiefly boys, came along the Strand, shouting, "No Peel!" "Down with the raw lobsters!" (the new police); "This way, my lads; we'll give it them!" At the back of the menageries at Charing Cross the police rushed upon them, and after a skirmish put them to flight. At seven o'clock the vast crowd by Temple Bar compelled every coachman and passenger in a coach, as a passport, to pull off his hat and shout "Huzza!" Stones were thrown, and attempts were made to close the gates of the Bar. The City marshals, however, compelled them to be reopened, and opposed the passage of the mob to the Strand, but the pass was soon forced. The rioters in Pickett Place pelted the police with stones and pieces of wood, broken from the scaffolding of the Law Institute, then building in Chancery Lane. Another mob of about 500 persons ran up Piccadilly to Apsley House and hissed and hooted the stubborn, unprogressive old Duke, Mr. Peel, and the police; the constables, however, soon dispersed them. The same evening dangerous mobs collected in Bethnal Green, Spitalfields, and Whitechapel, one party of them displaying tricoloured flags. They broke a lamp and a window or two, but did little else. Alas for poor Sir Claudius and his profound computations! His 2,284 fighting loyal men dwindled down to 600, including even those strange hybrids, the firemen-watermen; and as for the gallant Lumber Troop, they were nowhere visible to the naked eye.
To Bolt Court that scourge of King George III., William Cobbett, came from Fleet Street to sell his Indian corn, for which no one cared, and to print and publish his twopenny Political Register, for which the London Radicals of that day hungered. Nearly opposite the office of "this good hater," says Mr. Timbs, Wright (late Kearsley) kept shop, and published a searching criticism on Cobbett's excellent English Grammar as soon as it appeared. We only wonder that Cobbett did not reply to him as Johnson did to a friend after he knocked Osborne (the grubbing bookseller of Gray's Inn Gate) down with a blow—"Sir, he was impertinent, and I beat him."
A short biographical sketch of Cobbett will not be inappropriate here. This sturdy Englishman, born in the year 1762, was the son of an honest and industrious yeoman, who kept an inn called the "Jolly Farmer," at Farnham, in Surrey. "My first occupation," says Cobbett, "was driving the small birds from the turnip seed and the rooks from the peas. When I first trudged a-field with my wooden bottle and my satchel over my shoulder, I was hardly able to climb the gates and stiles." In 1783 the restless lad (a plant grown too high for the pot) ran away to London, and turned lawyer's clerk. At the end of nine months he enlisted, and sailed for Nova Scotia. Before long he became sergeant-major, over the heads of thirty other non-commissioned officers. Frugal and diligent, the young soldier soon educated himself. Discharged at his own request in 1791, he married a respectable girl, to whom he had before entrusted £150 hard-earned savings. Obtaining a trial against four officers of his late regiment for embezzlement of stores, for some strange reason Cobbett fled to France on the eve of the trial, but finding the king of that country dethroned, he started at once for America. At Philadelphia he boldly began as a high Tory bookseller, and denounced Democracy in his virulent "Porcupine Papers." Finally, overwhelmed with actions for libel, Cobbett in 1800 returned to England. Failing with a daily paper and a bookseller's shop, Cobbett then started his Weekly Register, which for thirty years continued to express the changes of his honest but impulsive and vindictive mind. Gradually—it is said, owing to some slight shown him by Pitt (more probably from real conviction)—Cobbett grew Radical and progressive, and in 1809 was fined £500 for libels on the Irish Government. In 1817 he was fined £1,000 and imprisoned two years for violent remarks about some Ely militiamen who had been flogged under a guard of fixed bayonets. This punishment he never forgave. He followed up his Register by his Twopenny Trash, of which he eventually sold 100,000 a number. The Six Acts being passed—as he boasted, to gag him—he fled, in 1817, again to America. The persecuted man returned to England in 1819, bringing with him, much to the amusement of the Tory lampooners, the bones of that foul man, Tom Paine, the infidel, whom (in 1796) this changeful politician had branded as "base, malignant, treacherous, unnatural, and blasphemous." During the Queen Caroline trial Cobbett worked heart and soul for that questionable martyr. He went out to Shooter's Hill to welcome her to London, and boasted of having waved a laurel bough above her head.
In 1825 he wrote a scurrilous "History of the Reformation" (by many still attributed to a priest), in which he declared Luther, Calvin, and Beza to be the greatest ruffians that ever disgraced the world. In his old age, too late to be either brilliant or useful, Cobbett got into Parliament, being returned in 1832 (thanks to the Reform Bill) member for Oldham. He died at his house near Farnham, in 1835. Cobbett was an egotist, it must be allowed, and a violent-tempered, vindictive man; but his honesty, his love of truth and liberty, few who are not blinded by party opinion can doubt. His writings are remarkable for vigorous and racy Saxon, as full of vituperation as Rabelais's, and as terse and simple as Swift's.
Mr. Grant, in his pleasant book, "Random Recollections of the House of Commons," written circa 1834, gives us an elaborate full-length portrait of old Cobbett. He was, he says, not less than six feet high, and broad and athletic in proportion. His hair was silver-white, his complexion ruddy as a farmer's. Till his small eyes sparkled with laughter, he looked a mere dullpated clodpole. His dress was a light, loose, grey tail-coat, a white waistcoat, and sandy kerseymere breeches, and he usually walked about the House with both his hands plunged into his breeches pockets. He had an eccentric, half-malicious way of sometimes suddenly shifting his seat, and on one important night, big with the fate of Peel's Administration, deliberately anchored down in the very centre of the disgusted Tories and at the very back of Sir Robert's bench, to the infinite annoyance of the somewhat supercilious party.
We next penetrate into Gough Square, in search of the great lexicographer.
As far as can be ascertained from Boswell, Dr. Johnson resided at Gough Square from 1748 to 1758, an eventful period of his life, and one of struggle, pain, and difficulty. In this gloomy side square near Fleet Street, he achieved many results and abandoned many hopes. Here he nursed his hypochondria—the nightmare of his life —and sought the only true relief in hard work. Here he toiled over books, drudging for Cave and Dodsley. Here he commenced both the Rambler and the Idler, and formed his acquaintance with Bennet Langton. Here his wife died, and left him more than ever a prey to his natural melancholy; and here he toiled on his great work, the Dictionary, in which he and six amanuenses effected what it took all the French Academicians to perform for their language.
A short epitome of what this great man accomplished while in Gough Square will clearly recall to our readers his way of life while in that locality. In 1749, Johnson formed a quiet club in Ivy Lane, wrote that fine paraphrase of Juvenal, "The Vanity of Human Wishes," and brought out, with dubious success, under Garrick's auspices, his tragedy of Irene. In 1750, he commenced the Rambler. In 1752, the year his wife died, he laboured on at the Dictionary. In 1753, he became acquainted with Bennet Langton. In 1754 he wrote the life of his early patron, Cave, who died that year. In 1755, the great Dictionary, begun in 1747, was at last published, and Johnson wrote that scathing letter to the Earl of Chesterfield, who, too late, thrust upon him the patronage the poor scholar had once sought in vain. In 1756, the still struggling man was arrested for a paltry debt of £5 18s., from which Richardson the worthy relieved him. In 1758, when he began the Idler, Johnson is described as "being in as easy and pleasant a state of existence as constitutional unhappiness ever permitted him to enjoy."
While the Dictionary was going forward, "Johnson," says Boswell, "lived part of the time in Holborn, part in Gough Square (Fleet Street); and he had an upper room fitted up like a countinghouse for the purpose, in which he gave to the copyists their several tasks. The words, partly taken from other dictionaries and partly supplied by himself, having been first written down with space left between them, he delivered in writing their etymologies, definitions, and various significations. The authorities were copied from the books themselves, in which he had marked the passages with a black-lead pencil, the traces of which could be easily effaced. I have seen several of them in which that trouble had not been taken, so that they were just as when used by the copyists. It is remarkable that he was so attentive to the choice of the passages in which words were authorised, that one may read page after page of his Dictionary with improvement and pleasure; and it should not pass unobserved, that he has quoted no author whose writings had a tendency to hurt sound religion and morality."
To this account Bishop Percy adds a note of great value for its lucid exactitude. "Boswell's account of the manner in which Johnson compiled his Dictionary," he says, "is confused and erroneous. He began his task (as he himself expressly described to me) by devoting his first care to a diligent perusal of all such English writers as were most correct in their language, and under every sentence which he meant to quote he drew a line, and noted in the margin the first letter of the word under which it was to occur. He then delivered these books to his clerks, who transcribed each sentence on a separate slip of paper and arranged the same under the word referred to. By these means he collected the several words, and their different significations, and when the whole arrangement was alphabetically formed, he gave the definitions of their meanings, and collected their etymologies from Skinner, and other writers on the subject." To these accounts, Hawkins adds his usual carping, pompous testimony. "Dr. Johnson," he says, "who, before this time, together with his wife, had lived in obscurity, lodging at different houses in the courts and alleys in and about the Strand and Fleet Street, had, for the purpose of carrying on this arduous work, and being near the printers employed in it, taken a handsome house in Gough Square, and fitted up a room in it with books and other accommodations for amanuenses, who, to the number of five or six, he kept constantly under his eye. An interleaved copy of "Bailey's Dictionary," in folio, he made the repository of the several articles, and these he collected by incessantly reading the best authors in our language, in the practice whereof his method was to score with a black-lead pencil the words by him selected. The books he used for this purpose were what he had in his own collection, a copious but a miserably ragged one, and all such as he could borrow; which latter, if ever they came back to those that lent them, were so defaced as to be scarce worth owning, and yet some of his friends were glad to receive and entertain them as curiosities."
"Mr. Burney," says Boswell, "during a visit to the capital, had an interview with Johnson in Gough Square, where he dined and drank tea with him, and was introduced to the acquaintance of Mrs. Williams. After dinner Mr. Johnson proposed to Mr. Burney to go up with him into his garret, which being accepted, he found there about five or six Greek folios, a poor writing-desk, and a chair and a half. Johnson, giving to his guest the entire seat, balanced himself on one with only three legs and one arm. Here he gave Mr. Burney Mrs. Williams's history, and showed him some notes on Shakespeare already printed, to prove that he was in earnest. Upon Mr. Burney's opening the first volume at the Merchant of Venice he observed to him that he seemed to be more severe on Warburton than on Theobald. 'Oh, poor Tib!' said Johnson, 'he was nearly knocked down to my hands; Warburton stands between me and him.' 'But, sir,' said Mr. Burney, 'You'll have Warburton on your bones, won't you?' 'No, sir;' he'll not come out; he'll only growl in his den.' 'But do you think, sir, Warburton is a superior critic to Theobald?' 'Oh, sir, he'll make two-and-fifty Theobalds cut into slices! The worst of Warburton is that he has a rage for saying something when there's nothing to be said.' Mr. Burney then asked him whether he had seen the letter Warburton had written in answer to a pamphlet addressed 'to the most impudent man alive.' He answered in the negative. Mr. Burney told him it was supposed to be written by Mallet. A controversy now raged between the friends of Pope and Bolingbroke, and Warburton and Mallet were the leaders of the several parties. Mr. Burney asked him then if he had seen Warburton's book against Bolingbroke's philosophy! 'No, sir; I have never read Bolingbroke's impiety, and therefore am not interested about its refutation.'"
Goldsmith appears to have resided at No. 6, Wine Office Court from 1760 to 1762, during which period he earned a precarious livelihood by writing for the booksellers.
They still point out Johnson and Goldsmith's favourite seats in the north-east corner of the window of that cozy though utterly unpretentious tavern, the "Cheshire Cheese," in this court.
It was while living in Wine Office Court that Goldsmith is supposed to have partly written that delightful novel "The Vicar of Wakefield," which he had begun at Canonbury Tower. We like to think that, seated at the "Cheese," he perhaps espied and listened to the worthy but credulous vicar and his gosling son attending to the profound theories of the learned and philosophic but shifty Mr. Jenkinson. We think now by the window, with a cross light upon his coarse Irish features, and his round prominent brow, we see the watchful poet sit eyeing his prey, secretly enjoying the grandiloquence of the swindler and the admiration of the honest country parson.
"One day," says Mrs. Piozzi, "Johnson was called abruptly from our house at Southwark, after dinner, and, returning in about three hours, said he had been with an enraged author, whose landlady pressed him within doors while the bailiffs beset him without; that he was drinking himself drunk with Madeira to drown care, and fretting over a novel which, when finished, was to be his whole fortune; but he could not get it done for distraction, nor dared he stir out of doors to offer it for sale. Mr. Johnson, therefore," she continues, "sent away the bottle and went to the bookseller, recommending the performance, and devising some immediate relief; which, when he brought back to the writer, the latter called the woman of the house directly to partake of punch and pass their time in merriment. It was not," she concludes, "till ten years after, I dare say, that something in Dr. Goldsmith's behaviour struck me with an idea that he was the very man; and then Johnson confessed that he was so."
"A more scrupulous and patient writer," says the admirable biographer of the poet, Mr. John Forster, "corrects some inaccuracies of the lively little lady, and professes to give the anecdote authentically from Johnson's own exact narration. 'I received one morning,' Boswell represents Johnson to have said, 'a message from poor Goldsmith, that he was in great distress, and, as it was not in his power to come to me, begging that I would come to him as soon as possible. I sent him a guinea, and promised to come to him directly. I accordingly went as soon as I was dressed, and found that his landlady had arrested him for his rent, at which he was in a violent passion. I perceived that he had already changed my guinea, and had got a bottle of Madeira and a glass before him. I put the cork into the bottle, desired he would be calm, and began to talk to him of the means by which he might be extricated. He then told me that he had a novel ready for the press, which he produced to me. I looked into it and saw its merits, told the landlady I should soon return, and, having gone to a bookseller, sold it for £60. I brought Goldsmith the money, and he discharged his rent, not without rating his landlady in a high tone for having used him so ill.'"
The arrest is plainly connected with Newbery's reluctance to make further advances, and of all Mrs. Fleming's accounts found among Goldsmith's papers, the only one unsettled is that for the summer months preceding the arrest. The manuscript of the novel seems by both statements (in which the discrepancies are not so great but that Johnson himself may be held accountable for them) to have been produced reluctantly, as a last resource; and it is possible, as Mrs. Piozzi intimates, that it was still regarded as unfinished. But if strong adverse reasons had not existed, Johnson would surely have carried it to the elder Newbery. He did not do this. He went with it to Francis Newbery, the nephew; does not seem to have given a very brilliant account of the "merit" he had perceived in it—four years after its author's death he told Reynolds that he did not think it would have had much success—and rather with regard to Goldsmith's immediate want than to any confident sense of the value of the copy, asked and obtained the £60. "And, sir," he said afterwards "a sufficient price, too, when it was sold, for then the fame of Goldsmith had not been elevated, as it afterwards was, by his 'Traveller,' and the bookseller had faint hopes of profit by his bargain. After 'The Traveller,' to be sure, it was accidentally worth more money."

GOUGH SQUARE (see page 118).
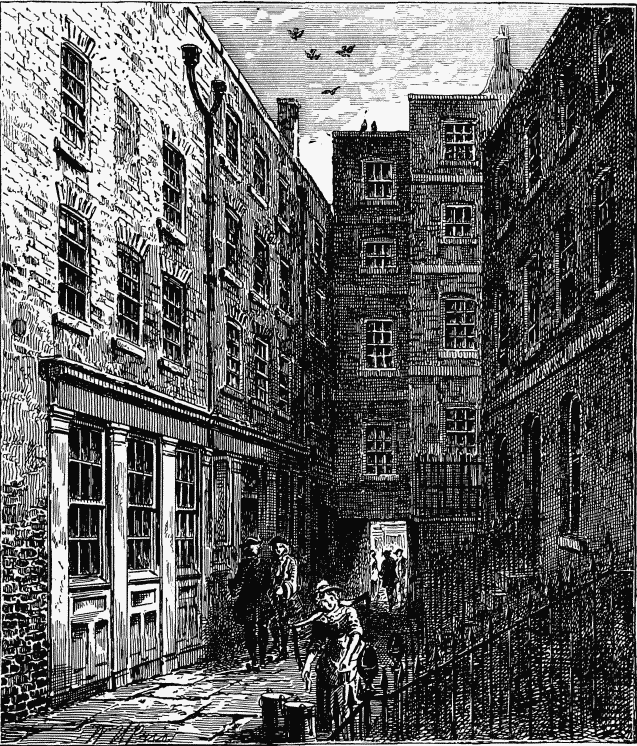
WINE OFFICE COURT AND THE "CHESHIRE CHEESE" (see page 122).
On the poem, meanwhile, the elder Newbery had consented to speculate, and this circumstance may have made it hopeless to appeal to him with a second work of fancy. For, on that very day of the arrest, "The Traveller" lay completed in the poet's desk. The dream of eight years, the solace and sustainment of his exile and poverty, verged at last to fulfilment or extinction, and the hopes and fears which centred in it doubtless mingled on that miserable day with the fumes of the Madeira. In the excitement of putting it to press, which followed immediately after, the nameless novel recedes altogether from the view, but will reappear in due time. Johnson approved the verses more than the novel; read the proof-sheets for his friend; substituted here and there, in more emphatic testimony of general approval, a line of his own; prepared a brief but hearty notice for the Critical Review, which was to appear simultaneously with the poem, and, as the day of publication drew near, bade Goldsmith be of good heart.
Oliver Goldsmith came first to London in 1756, a raw Irish student, aged twenty-eight. He was just fresh from Italy and Switzerland. He had heard Voltaire talk, had won a degree at Louvaine or Padua, had been "bear leader" to the stingy nephew of a rich pawnbroker, and had played the flute at the door of Flemish peasants for a draught of beer and a crust of bread. No city of golden pavement did London prove to those worn and dusty feet. Almost a beggar had Oliver been, then an apothecary's journeyman and quack doctor, next a reader of proofs for Richardson, the novelist and printer; after that a tormented and jaded usher at a Peckham school; last, and worst of all, a hack writer of articles for Griffith's Monthly Review, then being opposed by Smollett in a rival publication. In Green Arbour Court Goldsmith spent the roughest part of the toilsome years before he became known to the world. There he formed an acquaintance with Johnson and his set, and wrote essays for Smollett's British Magazine.
Wine Office Court is supposed to have derived its name from an office where licenses to sell wine were formerly issued. "In this court," says Mr. Noble, "once flourished a fig tree, planted a century ago by the Vicar of St. Bride's, who resided, with an absence of pride suitable, if not common, to Christianity, at No. 12. It was a slip from another exile of a tree, formerly flourishing, in a sooty kind of grandeur, at the sign of the 'Fig Tree,' in Fleet Street. This tree was struck by lightning in 1820, but slips from the growing stump were planted in 1822, in various parts of England."
The old-fashioned and changeless character of the "Cheese," in whose low-roofed and sanded rooms Goldsmith and Johnson have so often hung up their cocked hats and sat down facing each other to a snug dinner, not unattended with punch, has been capitally sketched by a modern essayist, who possesses a thorough knowledge of the physiology of London. In an admirable paper entitled "Brain Street," Mr. George Augustus Sala thus describes Wine Office Court and the "Cheshire Cheese":—
"The vast establishments," says Mr. Sala, "of Messrs. Pewter & Antimony, typefounders (Alderman Antimony was Lord Mayor in the year '46); of Messrs. Quoin, Case, & Chappell, printers to the Board of Blue Cloth; of Messrs. Cutedge & Treecalf, bookbinders; with the smaller industries of Scawper & Tinttool, wood-engravers; and Treacle, Gluepot, & Lampblack, printingroller makers, are packed together in the upper part of the court as closely as herrings in a cask. The 'Cheese' is at the Brain Street end. It is a little lop-sided, wedged-up house, that always reminds you, structurally, of a highshouldered man with his hands in his pockets. It is full of holes and corners and cupboards and sharp turnings; and in ascending the stairs to the tiny smoking-room you must tread cautiously, if you would not wish to be tripped up by plates and dishes, momentarily deposited there by furious waiters. The waiters at the 'Cheese' are always furious. Old customers abound in the comfortable old tavern, in whose sanded-floored eating-rooms a new face is a rarity; and the guests and the waiters are the oldest of familiars. Yet the waiter seldom fails to bite your nose off as a preliminary measure when you proceed to pay him. How should it be otherwise when on that waiter's soul there lies heavy a perpectual sense of injury caused by the savoury odour of steaks, and 'muts' to follow; of cheese-bubbling in tiny tins—the 'specialty' of the house; of floury potatoes and fragrant green peas; of cool salads, and cooler tankards of bitter beer; of extra-creaming stout and 'goes' of Cork and 'rack,' by which is meant gin; and, in the winter-time, of Irish stew and rump-steak pudding, glorious and grateful to every sense? To be compelled to run to and fro with these succulent viands from noon to late at night, without being able to spare time to consume them in comfort—where do waiters dine, and when, and how?—to be continually taking other people's money only for the purpose of handing it to other people—are not these grievances sufficient to crossgrain the temper of the mildest-mannered waiter? Somebody is always in a passion at the 'Cheese:' either a customer, because there is not fat enough on his 'point'-steak, or because there is too much bone in his mutton-chop; or else the waiter is wrath with the cook; or the landlord with the waiter, or the barmaid with all. Yes, there is a barmaid at the 'Cheese,' mewed up in a box not much bigger than a birdcage, surrounded by groves of lemons, 'ones' of cheese, punch-bowls, and cruets of mushroom-catsup. I should not care to dispute with her, lest she should quoit me over the head with a punch-ladle, having a William-theThird guinea soldered in the bowl.
"Let it be noted in candour that Law finds its way to the 'Cheese' as well as Literature; but the Law is, as a rule, of the non-combatant and, consequently, harmless order. Literary men who have been called to the bar, but do not practise; briefless young barristers, who do not object to mingling with newspaper men; with a sprinkling of retired solicitors (amazing dogs these for old port-wine; the landlord has some of the same bin which served as Hippocrene to Judge Blackstone when he wrote his 'Commentaries')—these make up the legal element of the 'Cheese.' Sharp attorneys in practice are not popular there. There is a legend that a process-server once came in at a back door to serve a writ; but being detected by a waiter, was skilfully edged by that wary retainer into Wine Bottle Court, right past the person on whom he was desirous to inflict the 'Victoria, by the grace, &c.' Once in the court, he was set upon by a mob of inky-faced boys just released from the works of Messrs. Ball, Roller, & Scraper, machine printers, and by the skin of his teeth only escaped being converted into 'pie.'"
Mr. William Sawyer has also written a very admirable sketch of the "Cheese" and its oldfashioned, conservative ways, which we cannot resist quoting:—
"We are a close, conservative, inflexible body —we, the regular frequenters of the 'Cheddar,'" says Mr. Sawyer. "No new-fangled notions, new usages, new customs, or new customers for us. We have our history, our traditions, and our observances, all sacred and inviolable. Look around! There is nothing new, gaudy, flippant, or effeminately luxurious here. A small room with heavily-timbered windows. A low planked ceiling. A huge, projecting fire-place, with a great copper boiler always on the simmer, the sight of which might have roused even old John Willett, of the 'Maypole,' to admiration. High, stiff-backed, inflexible 'settles,' hard and grainy in texture, box off the guests, half-a-dozen each to a table. Sawdust covers the floor, giving forth that peculiar faint odour which the French avoid by the use of the vine sawdust with its pleasant aroma. The only ornament in which we indulge is a solitary picture over the mantelpiece, a full-length of a now departed waiter, whom in the long past we caused to be painted, by subscription of the whole room, to commemorate his virtues and our esteem. He is depicted in the scene of his triumphs—in the act of giving change to a customer. We sit bolt upright round our tables, waiting, but not impatient. A time-honoured solemnity is about to be observed, and we, the old stagers, is it for us to precipitate it? There are men in this room who have dined here every day for a quarter of a century —aye, the whisper goes that one man did it even on his wedding-day! In all that time the more staid and well-regulated among us have observed a steady regularity of feeding. Five days in the week we have our 'Rotherham steak'—that mystery of mysteries—or our 'chop and chop to follow,' with the indispensable wedge of Cheddar—unless it is preferred stewed or toasted—and on Saturday decorous variety is afforded in a plate of the worldrenowned 'Cheddar' pudding. It is of this latter luxury that we are now assembled to partake, and that with all fitting ceremony and observance. As we sit, like pensioners in hall, the silence is broken only by a strange sound, as of a hardly human voice, muttering cabalistic words, 'Ullo mul lum de loodle wumble jum!' it cries, and we know that chops and potatoes are being ordered for some benighted outsider, ignorant of the fact that it is pudding-day."